Abstract
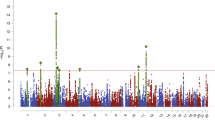
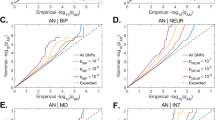
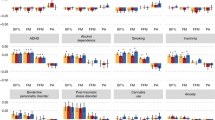
There is significant evidence for genetic factors in the susceptibility to anorexia nervosa (AN). Previously genetic variation in the estrogen receptor 2 gene (ESR2) has been studied, however no strong evidence of association with AN has been found. In the present study variation in the estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) and ESR2 genes was examined. Estrogen receptors have been localised to areas of the brain involved in behaviour and regulation of food intake. The anorexic effects of estrogen are accentuated by stress and thus it is postulated that variation in the estrogen receptors may contribute to the genetic susceptibility to AN in females. A cohort of 170 female, Caucasian AN sufferers and 152 female controls were typed for dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms in both ESR1 and ESR2 and two further SNPs at each locus. Variation at ESR1 was not associated with AN. However an association was found at the ESR2 locus with the heterozygous genotype of the G1082A polymorphism and AN but not with any of the other ESR2 polymorphisms analysed. Analysis of haplotypes at ESR1 and ESR2 showed no significant evidence of association with AN suggesting that the variability in ESR2 alone may contribute to the genetic susceptibility to AN.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halmi KA, Casper RC, Eckert ED, Goldberg SC, Davis JM . Unique features associated with age of onset of anorexia nervosa Psychiatry Res 1979 1: 209–215
Dagnault A, Richard D . Involvement of the medial preoptic area in the anorectic action of estrogens Am J Physiol 1997 272: R311–R317
Licino J, Wong M-L, Gold PW . The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in anorexia nervosa Psychiatry Res 1996 62: 75–83
Heinrichs SC, Menzaghi F, Merlo Pich E, Britton KT, Koob G . The role of CRF in behavioural aspects of stress Ann NY Acad Sci 1995 771: 92–104
Strakis CA, Chrousos GP . Neuroendocrinology and pathophysiology of the stress system Ann NY Acad Sci 1995 771: 1–18
Wade GN, Gray JM . Gonodal effects on food intake and adiposity. A metabolic hypothesis Physiol Behav 1979 22: 583–593
Piva R, Bianchi N, Aguiari GL, Gambari R, Del Sonno L . Sequencing of an RNA transcript of the human estrogen receptor gene: evidence for a new transcriptional event J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1993 46: 531–538
Mosselman S, Polman J, Dijkema R . ER beta: identification and characterisation of a novel human estrogen receptor FEBS Lett 1996 392: 49–53
Rosenkranz K, Hinney A, Ziegler A, Hermann H, Fichter M, Mayer H et al. Systematic mutation screening of the estrogen receptor beta gene in probands of different weight extremes: identification of several genetic variants JCE & M 1998 12: 4524–4527
Ogawa S, Luhbahn DB, Korach KS, Pfaff DW . Aggressive behaviours of transgenic estrogen-knockout male mice Ann NY Acad Sci 1996 794: 384–385
Commings DE, Muhleman D, Johnson P, MacMurray JP . Potential role of the estrogen receptor gene (ESR1) in anxiety Mol Psychiatry 1999 4: 374–377
Stevens R . Estradiol benzoate potentiates the effects of body restraint in suppressing food intake and reducing body weight in rats Physiol Behav 1989 45: 1–5
Shughrue PJ, Merchenthaler I . Evidence for the novel estrogen binding sites in the rat hippocampus Neuroscience 2000 99: 605–612
Cowley SM, Hoare S, Mosselmann S, Parker MG . Estrogen receptors α and β form heterodimers on DNA J Biol Chem 1997 272: 19858–19862
Yaich L, Dupont WD, Cavener DR, Parl FF . Analysis of the PvuII restriction-fragment-length-polymorphism and exon structure of the estrogen-receptor gene in breast-cancer and peripheral-blood Cancer Res 1992 52: 77–83
Zuppan PJ, Hall JM, Ponglikitmongkol M, Spielman R, King MC . Polymorphisms at the estrogen-receptor (ESR) locus and linkage relationships on chromosome-6Q Cytogenet Cell Genet 1989 51: 1116
Ogawa S, Hosoi T, Shiraki M, Orimo H, Emi M, Muramatsu M et al. Association of the estrogen receptor β gene polymorphism with bone mineral density Biochem Biophys Res Com 2000 269: 537–541
del Sonno L, Aguiari GL, Piva R . Dinuclotide repeat polymorphism in the human estrogen receptor (ESR) gene Hum Mol Genet 1992 1: 354
Sham PC, Curtis D . Monte Carlo test for association between disease and alleles at highly polymorphic loci Ann Hum Genet 1995 59: 97–105
Campbell MJ, Julious SA, Altman DG . Estimating sample sizes for binary, ordered categorical, and continuous outcome in two group comparisons BMJ 1995 311: 1145–1148
Garner DM, Olmstead MA, Polivy J . Development and validation of a multidimensional eating disorders inventory for anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa Int J of Eat Dis 1983 2: 15–34
Xie X, Ott J . Testing linkage disequilibrium between a disease gene and marker loci Am J Hum Genet 1993 53: 1107
Zhao JH, Curtis D, Sham PC . Model free analysis and permutation test for allelic associations Hum Hered 2000 50: 133–139
Acknowledgements
Research in the authors’ laboratory is supported by Northern and Yorkshire Regional Health Authority, Leeds Community and Mental Health Services NHS Trust and the West Riding Medical Research Trust. The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Jurg Ott (supported through grant MH44292 from the US National Institute for Mental Health) in performance of the haplotype analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eastwood, H., Brown, K., Markovic, D. et al. Variation in the ESR1 and ESR2 genes and genetic susceptibility to anorexia nervosa. Mol Psychiatry 7, 86–89 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000929
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000929
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between a common CYP17A1 haplotype and anxiety in female anorexia nervosa
Archives of Women's Mental Health (2013)
-
A systematic review of the relationship between polymorphic sites in the estrogen receptor-beta (ESR2) gene and breast cancer risk
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2011)
-
Estrogen Receptor 1 Gene (ESR1) is Associated with Restrictive Anorexia Nervosa
Neuropsychopharmacology (2010)
-
Impact of estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms and mRNA levels on obesity and lipolysis – a cohort study
BMC Medical Genetics (2007)
-
Estrogen receptor 2 and progesterone receptor gene polymorphisms and lipid levels in women with different hormonal status
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2005)