Abstract
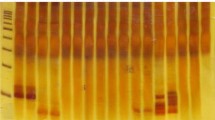
In many cases, particularly in retrospective studies, only formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples are available for molecular studies. DNA recovered from FFPE tissues generally consists of fragmented small target sequences with chemical alterations. Clonality analysis is not easy on FFPE samples, in fact, it requires even more experience than that of performed on fresh samples or is more complicated than most genomic PCR amplifications for somatic genes. In our study, we have performed a multi-parameter PCR evaluation investigating immunoglobulin heavy chain gene (IgH) and T-cell receptor gamma gene (TCRy) rearrangements on non-purified crude lysates of FFPE samples, in order to establish the significance of different variables on performance of PCR amplification. The results showed that a slight decrease in the concentration of primers in combination with a slight increase in MgCl2 andTaq polymerase concentrations, as well as the use diluted crude template and a standard amount of dNTPs can be the modifications of choice while adjusting IgH and TCRy clonality tests on poor quality DNA FFPE samples. Using our improved protocol, 74% (17/23) of the tested B-cell lymphomas and 68% (31/46) of the tested T-cell lymphomas demonstrated monoclonal PCR product, proving the applicability of our optimized method. Our experience may be of help during the optimization process in technically difficult cases as well as to determine which parameters and how should be changed to minimize false-negative and false-positive results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold A, Cossman J, Bakhsi A, et al: Immunoglobulin-gene rearrangements as unique clonal markers in human lymphoid neoplasms. N Engl J Med 309: 1593–1599, 1983
Korsmeyer SJ: B-lymphoid neoplasms: Immunoglobulin genes as molecular determinants of clonality, lineage, differentiation, and translocation. Adv Intern Med 33: 1–15, 1988
Van Dongen JJM, Langerak AW, Brüggemann M, et al: Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombination in suspect lymphoproliferations: Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 17:2257–2317, 2003
Trainor KJ, Brisco MJ, Story CJ, Morley AA: Monoclonality in B lymphoproliferative disorders detected at the DNA level. Blood 75:2220–2222, 1990
Lehman CM, Sarago C, Nasim S, et al: Comparison of PCR with Southern blot hybridization for the routine detection of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangements. Am J Clin Pathol 103:171–176, 1995
Hoeve MA, Krol ADG, Philippo K, et al: Limitations of clonality analysis of B cell proliferations using CDR3 polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Pathol:Mol Pathol 53:194–200, 2000
Inghirami G, Szabolcs MJ, Yee HT, et al: Detection of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement of B cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas and leukemias in fresh, unfixed and formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded tissue by polymerase chain reaction. Lab Invest 68: 746–757, 1993
McCarthy KP, Sloane JP, Kabarowski JHS, et al: A simplified method of detection of clonal rearrangements of the T-cell receptorg chain gene. Diagn Mol Pathol 1:173–179, 1992
Diss TC, Pan L, Peng H, et al: Sources of DNA for detecting B cell monoclonality using PCR. J Clin Pathol 47:493–496, 1994
Coates PJ, d’Ardenne AJ, Khan G, et al: Simplified procedures for applying the polymerase chain reaction to routinely fixed paraffin wax sections. J Clin Pathol 44:115–118, 1991
Kuppers R, Zhao M, Rajewsky K, et al: Detection of clonal B cell populations in paraffin-embedded tissues by polymerase chain reaction. Am J Pathol 143:230–239, 1993
Lorenzen J, Jux G, Zhao-Hohn M, et al: Detection of T-cell clonality in paraffin-embedded tissues. Diagn Mol Pathol 3: 93–99, 1994
Solomon MJ, Varshavsky A: Formaldehyde-mediated DNA-protein crosslinking: a probe for in vivo chromatin structures. PNAS 82:6470–6474, 1985
Ben-Ezra J, Johnson DA, Rossi J, et al. Effect of fixation on the amplification of nucleic acids from paraffin-embedded material by the polymerase chain reaction. J Histochem Cytochem 39:351–354, 1991
Bielawski K, Zaczek A, Lisowska U, et al: The suitability of DNA extracted from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues for double differential polymerase chain reaction analysis. Int J Mol Med 8:573–578, 2001
Srinivasan M, Sedmak D, Jewell S: Effect of fixatives and tissue processing on the content and integrity of nucleic acids. Am J Pathol 161:1961–1971, 2002
Metz B, Kersten GF, Hoogerhout P, et al: Identification of formaldehyde-induced modifications in proteins. Reactions with model peptides. J Biol Chem 279:6235–6243, 2004
Sepp R, Szabo I, Uda H, Sakamoto H: Rapid techniques for DNA extraction from routinely processed archival tissue for use in PCR. J Clin Pathol 47: 318–323, 1994
Sato Y, Sugie R, Tsuchiya B, et al: Comparison of the DNA extraction methods for polymerase chain reaction amplification from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues Diagn Mol Pathol 10:265–271, 2001
Shi S-R, Datar R, Liu C, et al: DNA extraction from archival formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: heat-induced retrieval in alkaline solution. Histochem Cell Biol 122: 211–218, 2004
Gonzalez MD, Gonzalez R, Lopez-Perez R, et al: Heteroduplex analysis of VDJ amplified segments from rearranged igh genes for clonality assessments in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. A comparison between different strategies. Hematologica 84:779–784, 1999
Gurbity TP, Bagdi E, Groen NA, et al: Increased sensitivity of Bcell clonality analysis in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded B-cell lymphoma samples using an enzyme blend with both 5′ → 3′ DNA polymerase and 3′ → 5′ exonuclease activity. Virchows Arch., 2003
Elenitoba-Johnson KSJ, Bohling SD, Mitchell RS, et al: PCR analysis of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene in polyclonal processes can yield pseudoclonal bands as an artifact of low B cell number. J Mol Diag 2:92–96, 2000
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, et al: Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239 487–499, 1988
Arber DA, Brazile RM, Bagg A, Bijwaard KE: Evaluation of T cell receptor testing in lymphoid neoplasms —Results of a multicenter study of 29 extracted DNA and paraffin-embedded samples. J Mol Diag 3:133–140, 2001
Bagg A, Braziel RM, Arber DA, Bijwaard KE, Chu AY: Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene analysis in lymphomas —A multi-center study demonstrating the heterogeneity of performance of polymerase chain reactions assays. J Mol Diag 4:81–89, 2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by the OTKA Research Fund (T046663 KON) and the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Bolyai Janos Research Fellowship (E.B.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bereczki, L., Kis, G., Bagdi, E. et al. Optimization of PCR amplification for B-and T-cell clonality analysis on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded samples. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 13, 209–214 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893501
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893501