Abstract
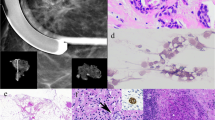
Seventy‐two patients underwent dye‐guided or dye‐ and gamma probe‐guided sentinel lymphadenectomy (SLND) followed by complete axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). The results of imprint cytology, frozen sections, and permanent sections of the sentinel lymph node (SLN) were compared to each other and to the histologic findings in the nonsentinel nodes. The SLN was identified in 62 (88%) of 72 patients. Evaluation of the SLN on the permanent sections yielded a diagnostic accuracy of 95%, a sensitivity of 89%, and a specificity of 100, although the reliability of SLN diagnosis using frozen sections or imprint cytology is limited. Therefore, it may be concluded that SLND with multiple sectioning and histopathologic examination of the SLNs can predict the presence or absence of axillary‐node metastases in patients with breast cancer. However, further studies will be needed to investigate the value of SLND in respect to the long‐term regional control and any possible detriment or benefit to survival, before it can replace routine ALND as the preferred staging operation for operable breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher B, Redmond C, Fisher ER, et al.: Ten-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing radical mastectomy and total mastectomy with or without radiation. N Engl J Med 312: 674–681, 1985
Lythgoe JP, Palmer MK: Manchester regional breast study - 5 and 10 years results. Br J Surg 69: 693–696, 1982
Cancer Research Campaign Work Party: Cancer Research Campaign (King's Cambridge) trial for early breast cancer. Lancet 2: 55–60, 1980
Senofsky GM, Moffat FL Jr, Davis K, et al.: Total axillary lymphadenectomy in the management of breast cancer. Arch Surg 126: 1336–1342, 1991
Donegan WL: Surgical clinical trials. Cancer 53: 691–699, 1984
Fentiman IS, Mansel RE: The axilla: not a no-go zone. Lancet 337: 221–223, 1991
Noguchi M, Miwa K, Michigishi T, et al.: The role of axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer management. Breast Cancer 4: 143–153, 1997
Kissin MW, Querci della Rovere G, Easton D, et al.: Risk of lymphedema following the treatment of breast cancer. Br J Surg 73: 580–584, 1986
Wazer DE, Erban JK, Robert NJ, et al.: Breast conservation in early women for clinically negative axillary lymph nodes without axillary dissection. Cancer 74: 878–883, 1994
Feigelson BJ, Acosta JA, Feigelson HS, et al.: T1 breast carcinoma in women 70 years of agc and older may not require axillary lymph node dissecton. Am J Surg 172: 487–490, 1996
Silverstein MJ, Gierson ED, Waisman JR, et al.: Axillary lymph node dissection for T1a breast carcinoma: Is it indicated? Cancer 73: 664–667, 1994
Cady B: The need to reexamine axillary lymph node dissection in invasive breast cancer. Cancer 73: 505–508, 1994
Chadha M, Chabon AB, Friedmann P, et al.: Predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in patients with T1 breast cancer. Cancer 73: 350–353, 1994
Greco M, Agresti R, Raselli R, et al.: Axillary dissection can be avoided in selected breast cancer patients: Analysis of 401 cases. Anticancer Res 16: 3913–3918, 1996
Noguchi M, Katev N, Miyazaki I: Diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 40: 283–293, 1996
Giuliano AE, Kirgan DM, Guenther JM, Morton DL: Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lyinphadenectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg 220: 391–401, 1994
Krag DN, Weaver DL, Alex C, Fairbank JT: Surgical resection and radiolocalization of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer using a gamma probe. Surg Oncol 2: 335–340, 1993
Albertini JA, Lyman GH, Cox C, et al.: Lymphatic mapping and sentinel node biopsy in the patient with breast cancer. JAMA 276: 1818–1822, 1996
Pijpers R, Meijer S, Hoekstra OS, et al.: Impact of lymphoscintigraphy on sentinel node identification with technetium-99m-colloidal albumin in breast cancer. J Nucl Med 38: 366–368, 1997
Veronesi U, Pagnelli G, Galimberti V, et al.: Sentinel-node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer with clinically negative lymphnode. Lancet 349: 1864–1867, 1997
Noguchi M, Kawahara F, Tsugawa K, et al.: Sentinel lymphadenectomy in breast cancer: alternative to routine axillary dissection. Breast Cancer 5: 1–7, 1998
Cox CE, Pendas S, Joseph E, et al.: Guidelines for sentinel node biopsy and lymphatic mapping of patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg 5: 645–653, 1998
Giuliano AE, Dale PS, Turner RR, et al.: Improved axillary staging of breast cancer with sentinel lymphadenectomy. Ann Surg 222: 394–401, 1995
International Union Against Cancer (UICC): Breast tumors (ICD-0 C-50). In: Sobin LH, Wittekind Ch (eds) TNM Classi-fication of Malignant Tumours. 5th edition. Wiley, New York, 1997, pp 123–130
Noguchi M, Tsugawa K, Kawahara F, et al.: Dye-guided sentinel lymphadenectomy in clinically node-negative or nodepositive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer 5: 381–387, 1998
O'Hea BJ, Hill ADK, El-Shirbiny AM, et al.: Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: Initial experience at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center. J Am Coll Surg 186: 423–427, 1998
Japan Breast Cancer Society: General rules for clinical and pathological recording of breast cancer. 12th edition. Kanehara, Tokyo, 1996: pp 19–34
The World Health Organization: The World Health Organization histological typing of breast tumors. Am J Clin Pathol 78: 806–816, 1982
Giuliano AE: Sentinel lymphadenectomy in primary breast carcinoma: an alternative to routine axillary dissection. J Surg Oncol 62(2): 75–77, 1996
Borgstein PJ, Pijpers R, Comans EF, et al.: Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: guidelines and pitfalls of lymphoscintigraphy and gamma probe detection. J Am Coll Surg 186: 275–283, 1998
Gulec SA, Moffat FL, Carrol RG, Krag DN: Gamma probe guided sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. GJ Nucl Med 41: 251–261, 1997
Kramer EL: Lymphoscintigraphy: radiopharmaceutical selection and methods. Nucl Med Biol 17: 57–63, 1990
Turner RR, Ollila DW, Krasne DL, Giuliano AG: Histopathologic validation of the sentinel lymph node hypothesis for breast carcinoma. Ann Surg 226: 271–278, 1997
Offodile R, Hoh C, Barsky SH, et al.: Minimally invasive breast carcinoma staging using lymphatic mapping with radiolabelled dextran. Cancer 82: 1704–1708, 1998
Giuliano AE: Sentinel lymphadenectomy: a new axillary staging procedure for primary breast carcinoma. Breast Dis 7: 16–17, 1996
Hadjiminas DJ, Burke M: Intraoperative assessment of nodal status in the selection of patients with breast cancer for axillary clearance. Br J Surg 81: 1615–1616, 1994
Fisher CJ, Boyle S, Burke M, Price AB: Intraoperative assessment of nodal status in the selection of patients with breast cancer for axillary clearance. Br J Surg 80: 457–458, 1993
McGuire WL: Adjuvant therapy of node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 320: 525–527, 1989
Mansour EG, Gray R, Shatila AH, et al.: Efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 320: 485–490, 1989
Fisher ER, Swamidoss S, Lee CH, et al.: Detection and significance of occult axillary node metastases in patients with invasive breast cancer. Cancer 42: 2025–2031, 1978
Kingsley WB, Peters GN, Check JH: What constitutes adequate study of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer? Ann Surg 201: 311–314, 1985
Ilainsworth PJ, Tjandra JJ, Stillwell RG, et al.: Detection and significance of occult metastasis in node-negative breast cancer. Br J Surg 80: 459–463, 1993
Noguchi M, Tsugawa K, Taniya T, Miwa K: The role of internal mammary lymph node metastases in the management of breast cancer. Breast Cancer 5: 117–125, 1998
Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, et al.: The sentinel node in breast cancer. A multicenter validation study. New Engl J Med 339: 941–946, 1998
Noguchi M: Comment on "Improved axillary staging of breast cancer with sentinel lymphadenectomy". Ann Surg 225: 126–127, 1997
Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Greco M, et al.: Prognosis of breast cancer patients after mastectomy and dissection of internal mammary nodes. Ann Surg 202: 702–707, 1985
Cody HS, Urban JA: Internal mammary node status: A major prognosticator in axillary node-negative breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2: 32–37, 1995
Cote RJ, Rosen PP, Old LJ, Osborne MP: Detection of bone marrow micrometastases in patients with early-stage breast cancer. Diag Oncol 1: 37–42, 1991
Dearnaley DP, Ormerod MG, Sloane JP: Micrometastases in breast cancer: Long-term follow-up of the first patient cohort. Eur J Cancer 27(12): 236–239, 1991
Mansi JL, Easton D, Berger U, et al.: Bone marrow micrometastases in primary breast cancer: Prognostic significance after 6 years' follow-up. Eur J Cancer 27(12): 1552–1555, 1991
Diel IJ, Kaufmann M, Goerner R, et al.: Detection of tumor cells in bone marrow of patients primary breat cancer: a prognostic factor for distant metastasis. J Clin Oncol 10(10): 1534–1539, 1992
Harbeck N, Untch M, Pache L, Eiermann W: Tumor cell detection in the bone marrow of breast cancer patients at primary therapy: results of a 3-year median follow-up. Br J Cancer 69: 566–571, 1994
Molino A, Pelosi G, Turazza M, et al.: Bone marrow micrometastases in 109 breast cancer patients: correlations with clinical and pathological features and prognosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 42: 23–30, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, M., Bando, E., Tsugawa, K. et al. Staging efficacy of breast cancer with sentinel lymphadenectomy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 57, 221–229 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006268426526
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006268426526