Abstract
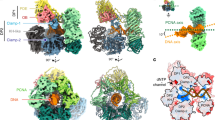
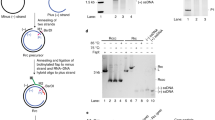
The mechanism of replication of the simian virus 40 (SV40) genome closely resembles that of cellular chromosomes, thereby providing an excellent model system for examining the enzymatic requirements for DNA replication1. Only one viral gene product, the large tumour antigen (large-T antigen), is required for viral replication2, so the majority of replication enzymes must be cellular. Indeed, a number of enzymatic activities associated with replication and the S phase of the cell cycle are induced upon SV40 infection3,4. Cell-free extracts derived from human cells, when supplemented with immunopurified SV40 large-T antigen support efficient replication of plasmids that contain the SV40 origin of DNA replication5–7. Using this system, a cellular protein of relative molecular mass 36,000 (Mr =36K) that is required for the elongation stage of SV40 DNA replication in vitro has been purified and identified as a known cell-cycle regulated protein, alternatively called the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) or cyclin8. It was noticed that, in its physical characteristics, PCNA closely resembles a protein that regulates the activity of calf thymus DNA polymerase-δ9. Here we show that PCNA and the polyrnerase-δ auxiliary protein have similar electrophoretic behaviour and are both recognized by anti-PCNA human autoantibodies. More importantly, both proteins are functionally equivalent; they stimulate SV40 DNA replication in vitro and increase the processivity of calf thymus DNA polymerase-δ. These results implicate a novel animal cell DNA polymerase, DNA polymerase-δ, in the elongation stage of replicative DNA synthesis in vitro.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DePamphilis, M. L. & Wassanman, P. M. in Organization and Replication of Viral DNA (ed. Kaplan, A. S.) 37–114 (CRC Press, Florida, 1982).
Tcgtmeyer, P. J. Virol 10, 591–598 (1972).
Sambrook, J. F. & Shatkin, A. S. J. Virol. 4, 719–726 (1969).
Kit, S., Piekarski, L. J. & Dubbs, D. R. J. gen. Virol. 1, 163–173 (1967).
Li, J. J. & Kelly, T. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 6973–6977 (1984).
Li, J. J. & Kelly, T. J. Molec cell. Biol. 5, 1238–1246 (1984).
Stillman, B. W. & Gluzman, Y. Molec cell. Biol. 5, 2051–2060 (1985).
Prelich, G., Kostura, M., Marshak, D. R., Mathews, M. B. & Stillman, B. Nature 326, 471–475 (1987).
Tan, C., Castillo, C., So, A. G. & Downey, K. M. J. biol. Chem. 261, 12310–12316 (1986).
Miyachi, K., Fritzler, M. J. & Tan, E. M. J. Immun. 121, 2228–2234 (1978).
Tan, E. M. Adv. Immun. 33, 167–240 (1982).
Bravo, R. Expl. Cell Res. 163, 287–293 (1986).
Celis, J. E. & Celis, A. Proc natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 3262–3266 (1985).
Mathews, M. B., Bernstein, R. M., Franza, B. R. Jr & Garrels, J. I. Nature 309, 374–376 (1984).
Pritchard, C. G., Weaver, D. T., Baril, E. F. & DePamphilis, M. L. J. biol. Chem. 258, 9810–9819 (1983).
Byrnes, J. J., Downey, K. M., Black, V. L. & So, A. G. Biochemistry 15, 2817–2823 (1976).
Lee, M. Y. W. T., Tan, C. K., Downey, K. M. & So, A.G. Biochemistry 23, 1906–1913 (1984).
Lee, M. Y. W. T., Toomey, N. L. & Wright, G. E. Nucleic Acids Res. 13, 8623–8630 (1985).
Byrnes, J. J. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 132, 628–634 (1985).
Crate, J. J., Wahl, A. F. & Bambara, R. A. Biochemistry 25, 26–36 (1986).
Fry, M. & Leob, L. A. Animal Cell DNA Polymerases (CRC press, Florida, 1986).
Murakami, Y., Wobbe, C. R., Weissbach, L., Dean, F. B. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 2869–2873 (1986).
Miller, M. R., Ulrich, R. G., Wang, T. S. & Korn, D. J. biol. Chem. 260, 134–138 (1985).
Kaczmarek, L., Miller, M. R., Hammond, R. A. & Mercer, W. E. J. biol. Chem. 261, 10802–10807 (1986).
Murakami, Y., Yasuda, H., Miyazawa, H., Hanaoka, F. & Yamada, M.-A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1761–1765 (1985).
Smale, S. T. & Tijan, R. Molec. Cell Biol. 6, 4077–4087 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prelich, G., Tan, CK., Kostura, M. et al. Functional identity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-δ auxiliary protein. Nature 326, 517–520 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/326517a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/326517a0
This article is cited by
-
High CD133 expression in proximal tubular cells in diabetic kidney disease: good or bad?
Journal of Translational Medicine (2024)
-
Dynamic patterns of gene expression and regulatory variation in the maize seed coat
BMC Plant Biology (2023)
-
Proteins in pregnant swine serum promote the African swine fever virus replication: an iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis
Virology Journal (2023)
-
The inner side of yeast PCNA contributes to genome stability by mediating interactions with Rad18 and the replicative DNA polymerase δ
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Allicin can suppress the activity of vascular endothelial cells probably by regulating JAK2/STAT3 pathway
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.