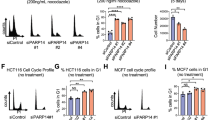
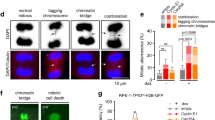
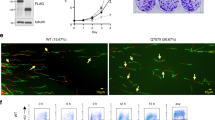
Abstract
THE p53 tumour-suppressor protein controls the expression of a gene encoding the p21 cyclin-dependent protein kinase (CDK) regulator1–6. Levels of p21 protein are increased in senescent cells and p21 overexpression blocks the growth of tumour cells1,3,7. In normal human cells, but not in many tumour cells, p21 exists in a quaternary complex with a cyclin, a CDK, and the proliferating-cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) 5,8. p21 controls CDK activity, thereby affecting cell-cycle control2–4,6, whereas PCNA functions in both DNA replication9–12 and repair13. Here we use simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro to show that p21 directly inhibits PCNA-dependent DNA replication in the absence of a cyclin/CDK. Furthermore, p21 blocks the ability of PCNA to activate DNA polymerase δ, the principal replicative DNA polymerase. This regulation results from a direct interaction between p21 and PCNA. Thus, during p53-mediated suppression of cell proliferation, p21 and PCNA may be important for coordinating cell-cycle progression, DNA replication and repair of damaged DNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Deiry, W. S. et al. Cell 75, 817–825 (1993).
Gu, Y., Turck, C. W. & Morgan, D. O. Nature 366, 707–710 (1993).
Harper, J. W., Adami, G. R., Wei, N., Keyomarsi, K. & Elledge, S. J. Cell 75, 805–816 (1993).
Xiong, Y. et al. Nature 366, 701–704 (1993).
Xiong, Y., Zhang, H. & Beach, D. Genes Dev. 7, 1572–1583 (1993).
Dulic, V. et al. Cell 76, 1013–1023 (1994).
Noda, A. F., Ning, Y., Venable, S., Pereira-Smith, O. M. & Smith, J. R. Expl Cell Res. 211, 90–98 (1994).
Xiong, Y., Zhang, H. & Beach, D. Cell 71, 505–514 (1992).
Prelich, G., Kostura, M., Marshak, D. R., Mathews, M. B. & Stillman, B. Nature 326, 471–475 (1987).
Prelich, G. & Stillman, B. Cell 53, 117–126 (1988).
Tsurimoto, T., Melendy, T. & Stillman, B. Nature 346, 534–539 (1990).
Waga, S. & Stillman, B. Nature 369, 207–212 (1994).
Shivji, M. K. K., Kenny, M. K. & Wood, R. D. Cell 69, 367–374 (1992).
Challberg, M. D. & Kelly, T. J. A. Rev. Biochem. 58, 671–717 (1989).
Stillman, B. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 5, 197–245 (1989).
Melendy, T. & Stillman, B. in Nucleic Acids and Molecular Biology Vol. VI (eds Eckstein, F. & Lilley, D. M. J.) 129–158 (Springer, Berlin, 1992).
Hurwitz, J., Dean, F. B., Kwong, A. D. & Lee, S.-H. J. biol. Chem. 265, 18043–18046 (1990).
Waga, S., Bauer, G. & Stillman, B. J. biol. Chem. 269, 10923–10934 (1994).
Stillman, B. W. & Gluzman, Y. Molec. cell. Biol. 5, 2051–2060 (1985).
Serrano, M., Hannon, G. J. & Beach, D. Nature 366, 704–707 (1993).
Tan, C.-K., Castillo, C., So, A. G. & Downey, K. M. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 12310–12316 (1986).
Bauer, G. A. & Burgers, P. M. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 7506–7510 (1988).
Kong, X.-P., Onrust, R., O'Donnell, M. & Kuriyan, J. Cell 69, 425–437 (1992).
Zhang, H., Xiong, Y. & Beach, D. Molec. Biol. Cell 4, 897–906 (1993).
Waseem, N. H., Labib, K., Nurse, P. & Lane, D. P. EMBO J. 11, 5111–5120 (1992).
Kastan, M. et al. Cell 71, 587–597 (1992).
Kuerbitz, S. J., Plunkett, B. S., Walsh, W. V. & Kastan, M. B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7491–7495 (1992).
Lu, X. & Lane, D. P. Cell 75, 765–778 (1993).
Tsurmoto, T. & Stillman, B. J. biol. Chem. 266, 1961–1968 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waga, S., Hannon, G., Beach, D. et al. The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature 369, 574–578 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/369574a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/369574a0
This article is cited by
-
Non-POU Domain-Containing Octomer-Binding (NONO) protein expression and stability promotes the tumorigenicity and activation of Akt/MAPK/β-catenin pathways in human breast cancer cells
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory virus 2 infection of the fetus results in multi-organ cell cycle suppression
Veterinary Research (2022)
-
Knockdown of the stem cell marker Musashi-1 inhibits endometrial cancer growth and sensitizes cells to radiation
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
p53 at the crossroad of DNA replication and ribosome biogenesis stress pathways
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
Inhibition of p21 activates Akt kinase to trigger ROS-induced autophagy and impacts on tumor growth rate
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.