Abstract
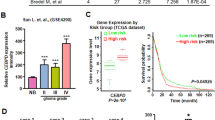
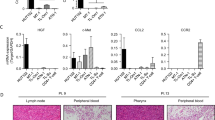
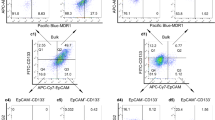
Successful treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is frequently hindered by the development of resistance to conventional chemotherapy resulting in disease relapse and high mortality. High expression of antiapoptotic and/or drug transporter proteins induced by oncogenic signaling pathways has been implicated in the development of chemoresistance in cancer. Previously, our studies showed that high expression of adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette drug transporter ABCG2 in DLBCL correlated inversely with disease- and failure-free survival. In this study, we have implicated activated hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway as a key factor behind high ABCG2 expression in DLBCL through direct upregulation of ABCG2 gene transcription. We have identified a single binding site for GLI transcription factors in the ABCG2 promoter and established its functionality using luciferase reporter, site-directed mutagenesis and chromatin-immunoprecipitation assays. Furthermore, in DLBCL tumor samples, significantly high ABCG2 and GLI1 levels were found in DLBCL tumors with lymph node involvement in comparison with DLBCL tumor cells collected from pleural and/or peritoneal effusions. This suggests a role for the stromal microenvironment in maintaining high levels of ABCG2 and GLI1. Accordingly, in vitro co-culture of DLBCL cells with HS-5 stromal cells increased ABCG2 mRNA and protein levels by paracrine activation of Hh signaling. In addition to ABCG2, co-culture of DLBCL cells with HS-5 cells also resulted in increase expression of the antiapoptotic proteins BCL2, BCL-xL and BCL2A1 and in induced chemotolerance to doxorubicin and methotrexate, drugs routinely used for the treatment of DLBCL. Similarly, activation of Hh signaling in DLBCL cell lines with recombinant Shh N-terminal peptide resulted in increased expression of BCL2 and ABCG2 associated with increased chemotolerance. Finally, functional inhibition of ABCG2 drug efflux activity with fumitremorgin C or inhibition of Hh signaling with cyclopamine-KAAD abrogated the stroma-induced chemotolerance suggesting that targeting ABCG2 and Hh signaling may have therapeutic value in overcoming chemoresistance in DLBCL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott BL, Colapietro AM, Barnes Y, Marini F, Andreeff M, Sorrentino BP . (2002). Low levels of ABCG2 expression in adult AML blast samples. Blood 100: 4594–4601.
Alexander DD, Mink PJ, Adami HO, Chang ET, Cole P, Mandel JS et al. (2007). The non-Hodgkin lymphomas: a review of the epidemiologic literature. Int J Cancer 120 (Suppl 12): 1–39.
Allikmets R, Schriml LM, Hutchinson A, Romano-Spica V, Dean M . (1998). A human placenta-specific ATP-binding cassette gene (ABCP) on chromosome 4q22 that is involved in multidrug resistance. Cancer Res 58: 5337–5339.
Ambudkar SV, Dey S, Hrycyna CA, Ramachandra M, Pastan I, Gottesman MM . (1999). Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39: 361–398.
Andreadis C, Gimotty PA, Wahl P, Hammond R, Houldsworth J, Schuster SJ et al. (2007). Members of the glutathione and ABC-transporter families are associated with clinical outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 109: 3409–3416.
Armitage JO . (2007). How I treat patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 110: 29–36.
Bailey-Dell KJ, Hassel B, Doyle LA, Ross DD . (2001). Promoter characterization and genomic organization of the human breast cancer resistance protein (ATP-binding cassette transporter G2) gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1520: 234–241.
Barnes EA, Heidtman KJ, Donoghue DJ . (2005). Constitutive activation of the shh-ptc1 pathway by a patched1 mutation identified in BCC. Oncogene 24: 902–915.
Baumann P, Mandl-Weber S, Volkl A, Adam C, Bumeder I, Oduncu F et al. (2009). Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitor A771726 (leflunomide) induces apoptosis and diminishes proliferation of multiple myeloma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 8: 366–375.
Benderra Z, Faussat AM, Sayada L, Perrot JY, Chaoui D, Marie JP et al. (2004). Breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein in 149 adult acute myeloid leukemias. Clin Cancer Res 10: 7896–7902.
Bhatia N, Thiyagarajan S, Elcheva I, Saleem M, Dlugosz A, Mukhtar H et al. (2006). Gli2 is targeted for ubiquitination and degradation by beta-TrCP ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem 281: 19320–19326.
Bigelow RL, Chari NS, Unden AB, Spurgers KB, Lee S, Roop DR et al. (2004). Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 mediated by the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway through gli-1. J Biol Chem 279: 1197–1205.
Bleau AM, Huse JT, Holland EC . (2009). The ABCG2 resistance network of glioblastoma. Cell Cycle 8: 2936–2944.
Candeil L, Gourdier I, Peyron D, Vezzio N, Copois V, Bibeau F et al. (2004). ABCG2 overexpression in colon cancer cells resistant to SN38 and in irinotecan-treated metastases. Int J Cancer 109: 848–854.
Damiani D, Tiribelli M, Michelutti A, Geromin A, Cavallin M, Fabbro D et al. (2010). Fludarabine-based induction therapy does not overcome the negative effect of ABCG2 (BCRP) over-expression in adult acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leuk Res 34: 942–945.
Dean M, Allikmets R . (2001). Complete characterization of the human ABC gene family. J Bioenerg Biomembr 33: 475–479.
Desch P, Asslaber D, Kern D, Schnidar H, Mangelberger D, Alinger B et al. (2010). Inhibition of GLI, but not smoothened, induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Oncogene 29: 4885–4895.
Dierks C, Grbic J, Zirlik K, Beigi R, Englund NP, Guo GR et al. (2007). Essential role of stromally induced hedgehog signaling in B-cell malignancies. Nat Med 13: 944–951.
Diestra JE, Scheffer GL, Catala I, Maliepaard M, Schellens JH, Scheper RJ et al. (2002). Frequent expression of the multi-drug resistance-associated protein BCRP/MXR/ABCP/ABCG2 in human tumours detected by the BXP-21 monoclonal antibody in paraffin-embedded material. J Pathol 198: 213–219.
Doyle LA, Yang W, Abruzzo LV, Krogmann T, Gao Y, Rishi AK et al. (1998). A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15665–15670.
Eichberger T, Sander V, Schnidar H, Regl G, Kasper M, Schmid C et al. (2006). Overlapping and distinct transcriptional regulator properties of the GLI1 and GLI2 oncogenes. Genomics 87: 616–632.
Fernandez M, Pino AM, Figueroa P, Rodriguez JP . (2010). The increased expression of receptor activator of nuclear-kappaB ligand (RANKL) of multiple myeloma bone marrow stromal cells is inhibited by the bisphosphonate ibandronate. J Cell Biochem 111: 130–137.
Fidler IJ . (2003). The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 453–458.
Fisher RI, Gaynor ER, Dahlberg S, Oken MM, Grogan TM, Mize EM et al. (1993). Comparison of a standard regimen (CHOP) with three intensive chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med 328: 1002–1006.
Gottesman MM . (2002). Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu Rev Med 53: 615–627.
Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE . (2002). Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 48–58.
Grigorieva I, Thomas X, Epstein J . (1998). The bone marrow stromal environment is a major factor in myeloma cell resistance to dexamethasone. Exp Hematol 26: 597–603.
Hegde GV, Peterson KJ, Emanuel K, Mittal AK, Joshi AD, Dickinson JD et al. (2008). Hedgehog-induced survival of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in a stromal cell microenvironment: a potential new therapeutic target. Mol Cancer Res 6: 1928–1936.
Honjo Y, Hrycyna CA, Yan QW, Medina-Perez WY, Robey RW, van de Laar A et al. (2001). Acquired mutations in the MXR/BCRP/ABCP gene alter substrate specificity in MXR/BCRP/ABCP-overexpressing cells. Cancer Res 61: 6635–6639.
Hu LL, Wang XX, Chen X, Chang J, Li C, Zhang Y et al. (2007). BCRP gene polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility and survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Carcinogenesis 28: 1740–1744.
Jerkeman M, Anderson H, Dictor M, Kvaloy S, Akerman M, Cavallin-Stahl E . (2004). Assessment of biological prognostic factors provides clinically relevant information in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma--a Nordic Lymphoma Group study. Ann Hematol 83: 414–419.
Kage K, Tsukahara S, Sugiyama T, Asada S, Ishikawa E, Tsuruo T et al. (2002). Dominant-negative inhibition of breast cancer resistance protein as drug efflux pump through the inhibition of S-S dependent homodimerization. Int J Cancer 97: 626–630.
Kawabata S, Oka M, Soda H, Shiozawa K, Nakatomi K, Tsurutani J et al. (2003). Expression and functional analyses of breast cancer resistance protein in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9: 3052–3057.
Kim JE, Singh RR, Cho-Vega JH, Drakos E, Davuluri Y, Khokhar FA et al. (2009). Sonic hedgehog signaling proteins and ATP-binding cassette G2 are aberrantly expressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol 22: 1312–1320.
Krishnamurthy P, Ross DD, Nakanishi T, Bailey-Dell K, Zhou S, Mercer KE et al. (2004). The stem cell marker Bcrp/ABCG2 enhances hypoxic cell survival through interactions with heme. J Biol Chem 279: 24218–24225.
Krishnamurthy P, Schuetz JD . (2006). Role of ABCG2/BCRP in biology and medicine. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46: 381–410.
Lwin T, Crespo LA, Wu A, Dessureault S, Shu HB, Moscinski LC et al. (2009). Lymphoma cell adhesion-induced expression of B cell-activating factor of the TNF family in bone marrow stromal cells protects non-Hodgkin/s B lymphoma cells from apoptosis. Leukemia 23: 170–177.
McMillin DW, Delmore J, Weisberg E, Negri JM, Geer DC, Klippel S et al. (2010). Tumor cell-specific bioluminescence platform to identify stroma-induced changes to anticancer drug activity. Nat Med 16: 483–489.
Miyake K, Mickley L, Litman T, Zhan Z, Robey R, Cristensen B et al. (1999). Molecular cloning of cDNAs which are highly overexpressed in mitoxantrone-resistant cells: demonstration of homology to ABC transport genes. Cancer Res 59: 8–13.
Mueller MM, Fusenig NE . (2004). Friends or foes—bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 839–849.
Murone M, Rosenthal A, de Sauvage FJ . (1999). Hedgehog signal transduction: from flies to vertebrates. Exp Cell Res 253: 25–33.
Ohsawa M, Ikura Y, Fukushima H, Shirai N, Sugama Y, Suekane T et al. (2005). Immunohistochemical expression of multidrug resistance proteins as a predictor of poor response to chemotherapy and prognosis in patients with nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncology 68: 422–431.
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, Werner T . (1995). MatInd and MatInspector: new fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 23: 4878–4884.
Queiroz KC, Ruela-de-Sousa RR, Fuhler GM, Aberson HL, Ferreira CV, Peppelenbosch MP et al. (2010). Hedgehog signaling maintains chemoresistance in myeloid leukemic cells. Oncogene 29: 6314–6322.
Rabindran SK, Ross DD, Doyle LA, Yang W, Greenberger LM . (2000). Fumitremorgin C reverses multidrug resistance in cells transfected with the breast cancer resistance protein. Cancer Res 60: 47–50.
Robey RW, Honjo Y, Morisaki K, Nadjem TA, Runge S, Risbood M et al. (2003). Mutations at amino-acid 482 in the ABCG2 gene affect substrate and antagonist specificity. Br J Cancer 89: 1971–1978.
Rocchi E, Khodjakov A, Volk EL, Yang CH, Litman T, Bates SE et al. (2000). The product of the ABC half-transporter gene ABCG2 (BCRP/MXR/ABCP) is expressed in the plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 271: 42–46.
Rodriguez C, Commes T, Robert J, Rossi JF . (1993). Expression of P-glycoprotein and anionic glutathione S-transferase genes in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Leuk Res 17: 149–156.
Sacedon R, Diez B, Nunez V, Hernandez-Lopez C, Gutierrez-Frias C, Cejalvo T et al. (2005). Sonic hedgehog is produced by follicular dendritic cells and protects germinal center B cells from apoptosis. J Immunol 174: 1456–1461.
Sarkadi B, Ozvegy-Laczka C, Nemet K, Varadi A . (2004). ABCG2—a transporter for all seasons. FEBS Lett 567: 116–120.
Sauerbrey A, Sell W, Steinbach D, Voigt A, Zintl F . (2002). Expression of the BCRP gene (ABCG2/MXR/ABCP) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 118: 147–150.
Schmittgen TD . (2001). Real-time quantitative PCR. Methods 25: 383–385.
Sims-Mourtada J, Izzo JG, Ajani J, Chao KS . (2007). Sonic Hedgehog promotes multiple drug resistance by regulation of drug transport. Oncogene 26: 5674–5679.
Sims-Mourtada J, Izzo JG, Apisarnthanarax S, Wu TT, Malhotra U, Luthra R et al. (2006). Hedgehog: an attribute to tumor regrowth after chemoradiotherapy and a target to improve radiation response. Clin Cancer Res 12: 6565–6572.
Singh RR, Cho-Vega JH, Davuluri Y, Ma S, Kasbidi F, Milito C et al. (2009). Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is activated in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancer Res 69: 2550–2558.
Singh RR, Kim JE, Davuluri Y, Drakos E, Cho-Vega JH, Amin HM et al. (2010). Hedgehog signaling pathway is activated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and contributes to tumor cell survival and proliferation. Leukemia 24: 1025–1036.
Stam RW, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, den Boer ML, Ebus ME, Janka-Schaub GE, Allen JD et al. (2004). Multidrug resistance genes in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Ara-C is not a substrate for the breast cancer resistance protein. Leukemia 18: 78–83.
Steinbach D, Sell W, Voigt A, Hermann J, Zintl F, Sauerbrey A . (2002). BCRP gene expression is associated with a poor response to remission induction therapy in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 16: 1443–1447.
Taipale J, Beachy PA . (2001). The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 411: 349–354.
To KK, Zhan Z, Bates SE . (2006). Aberrant promoter methylation of the ABCG2 gene in renal carcinoma. Mol Cell Biol 26: 8572–8585.
Tsunoda S, Okumura T, Ito T, Kondo K, Ortiz C, Tanaka E et al. (2006). ABCG2 expression is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology 71: 251–258.
Uggla B, Stahl E, Wagsater D, Paul C, Karlsson MG, Sirsjo A et al. (2005). BCRP mRNA expression v. clinical outcome in 40 adult AML patients. Leuk Res 29: 141–146.
Winklmayr M, Schmid C, Laner-Plamberger S, Kaser A, Aberger F, Eichberger T et al. (2010). Non-consensus GLI binding sites in Hedgehog target gene regulation. BMC Mol Biol 11: 2.
Yasuda S, Kobayashi M, Itagaki S, Hirano T, Iseki K . (2009). Response of the ABCG2 promoter in T47D cells and BeWo cells to sex hormone treatment. Mol Biol Rep 36: 1889–1896.
Yoh K, Ishii G, Yokose T, Minegishi Y, Tsuta K, Goto K et al. (2004). Breast cancer resistance protein impacts clinical outcome in platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: 1691–1697.
Yuen AR, Sikic BI . (1994). Multidrug resistance in lymphomas. J Clin Oncol 12: 2453–2459.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Susan E Bates (NIH) for providing the ABCG2 promoter luciferase constructs. We also thank Professor Michael G Rosenblum, Department of Experimental Therapeutics, MD Anderson Cancer Center for providing OCI-LY3 and OCI-LY10 cell lines. The primary tumor samples were provided by the Hematopathology and Lymphoma Tissue Banks of the UT MD Anderson Cancer Center (supported by the NCI/NIH Grant CA16672). This research was supported by funds from The Translational Grant of The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (to RRS and FV), K08 Physician-Scientist Award 1 K08 CA143151-01 (NIH) (to FV), SPORE Lymphoma Grant UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Lymphoma SPORE 1P50CA136411-01A1 (to FV) and Lauri Strauss Leukemia Foundation Grant award (to RRS and FV).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Kunkalla, K., Qu, C. et al. ABCG2 is a direct transcriptional target of hedgehog signaling and involved in stroma-induced drug tolerance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncogene 30, 4874–4886 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.195
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.195
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hedgehog signaling in tissue homeostasis, cancers, and targeted therapies
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
USP10 suppresses ABCG2-induced malignant characteristics of doxorubicin-resistant thyroid cancer by inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (2023)
-
Smoothened (SMO) regulates insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) levels and protein kinase B (AKT) localization and signaling
Laboratory Investigation (2022)
-
Three-dimensional models: a novel approach for lymphoma research
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2022)
-
GLI1 reduces drug sensitivity by regulating cell cycle through PI3K/AKT/GSK3/CDK pathway in acute myeloid leukemia
Cell Death & Disease (2021)