Abstract
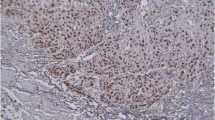
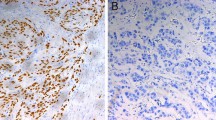
The aim of this study was to explore the relationship between p53 and cyclin A immunostaining in squamous carcinomas of the oesophagus. It has been shown that both these proteins are over-expressed in poorly differentiated endometrial carcinomas. Fifty oesophagectomy specimens were analysed for p53 and cyclin A immunoexpression. This was correlated with patient age and gender and tumor stage and grade. Forty-two percent of cases were p53 positive, while 94% of the squamous cancers expressed cyclin A protein. Neither protein showed any statistically significant correlation with clinicopathological parameters. This study has demonstrated that only 42% of oesophageal squamous carcinomas from South Africa express p53 protein, while the vast majority (94%) express cyclin A protein. Neither of these proteins showed any relationship to each other or any clinical feature or the tumor grade or stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stemmermann G, Heffelfinger SC, Noffsinger A, et al: The molecular biology of esophageal and gastric cancer and their precursors: oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and growth fac-tors. Hum Pathol 25:968–981, 1994.
Motokura T, Arnold A: Cyclins and oncogenesis. Biochima et Biphysica Acta 1155:63–78, 1993.
Shiozawa T, Xin L, Nikaido T, et al: Immunohistochemical detection of cyclin A with reference to p53 expression in endometrial endometrioid carcinomas. Int J Gynecol Pathol 16:348–353, 1997.
Hollstein MA, Metcalf RA, Welsh JA, et al: Frequent mutation of the p53 gene in human esophageal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9958–9961, 1990.
Meltzer SJ, Yin J, Huang Y, et al: Reduction to homozygosity involving p53 in esophageal cancers demonstrated by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4976–4980, 1991.
Uchino S, Saito T, Inomata M, et al: Prognostic significance of the p53 mutation in esophageal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 26:287–292, 1996.
Wang DY, Xiang YY, Tanaka M, et al: High prevalence of p53 protein expression in patients with esophageal cancer in Linxian, China and its relationship to progression and prognosis. Cancer 74:3089–3096, 1994.
Sarbia M, Porschen R, Borchard F, et al: p53 protein expression and prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer 74:2218–2223, 1994.
Shimaya K, Shiozaki H, Inoue M, et al: Significance of p53 expression as a prognostic factor in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Virchows Archiv Pathol Anat Histopathology 422:271–276, 1993.
Chetty R, Chetty S: Cyclin DI and retinoblastoma protein expression in oesophageal squamous carcinoma. J Clin Pathol: Mol Pathol 50:257–260, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
RC is funded by the Cancer Association of South Africa, University of Natal Research Fund and the Medical Research Council of South Africa.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chetty, R., Simelane, S. p53 and cyclin a protein expression in squamous carcinoma of the oesophagus. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 5, 193–196 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1053/paor.1999.0196
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/paor.1999.0196