Abstract
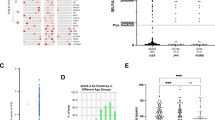
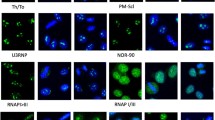
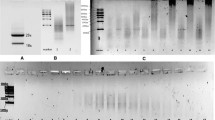
To identify a new diagnostic marker for the immune pathophysiology of aplastic anemia (AA), we screened sera of immune-mediated AA patients for the presence of antibodies (Abs) specific to proteins derived from a leukemia cell line UT-7 using two-dimensional electrophoresis followed by immunoblotting. The target proteins were identified by peptide mass fingerprinting. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) K was identified as a novel autoantigen. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay revealed high titers of anti-hnRNP K Abs in 85 (31%) of 273 patients with AA. Sixty-four patients received antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine after undergoing screening for anti-hnRNP K Ab, anti-DRS-1 Ab, anti-moesin Ab, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)-type cells. Twenty (87%) of 23 patients with the presence of anti-hnRNP K Abs responded to the immunosuppressive therapy (IST), while 19 (46%) of 41 patients without the presence of anti-hnRNP K Abs responded. A multivariate analysis showed only PNH-type cells and anti-hnRNP K Abs to be significant factors for the prediction of a good response to IST. The detection of anti-hnRNP K Abs as well as PNH-type cells may therefore be useful for diagnosing the immune pathophysiology of AA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenfeld SJ, Kimball J, Vining D, Young NS (1995) Intensive immunosuppression with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine as treatment for severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood 85(11):3058–3065
Bacigalupo A, Broccia G, Corda G, Arcese W, Carotenuto M, Gallamini A, Locatelli F, Mori PG, Saracco P, Todeschini G, Coser P, Iacopino P, Vanlint MT, Gluckman E (1995) Antilymphocyte globulin, cyclosporin, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with acquired severe aplastic anemia (SAA): a pilot study of the EBMT SAA Working Party. Blood 85(5):1348–1353
Maciejewski JP, Hibbs JR, Anderson S, Katevas P, Young NS (1994) Bone marrow and peripheral blood lymphocyte phenotype in patients with bone marrow failure. Exp Hematol 22(11):1102–1110
Nakao S, Yamaguchi M, Shiobara S, Yokoi T, Miyawaki T, Taniguchi T, Matsuda T (1992) Interferon-gamma gene expression in unstimulated bone marrow mononuclear cells predicts a good response to cyclosporine therapy in aplastic anemia. Blood 79(10):2532–2535
Sloand E, Kim S, Maciejewski JP, Tisdale J, Follmann D, Young NS (2002) Intracellular interferon-gamma in circulating and marrow T cells detected by flow cytometry and the response to immunosuppressive therapy in patients with aplastic anemia. Blood 100(4):1185–1191
Takami A, Nakao S, Tatsumi Y, Wang HB, Zeng WH, Yamazaki H, Yasue S, Shiobara S, Matsuda T, Mizoguchi H (1999) High inducibility of heat shock protein 72 (hsp72) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of aplastic anaemia patients: a reliable marker of immune-mediated aplastic anaemia responsive to cyclosporine therapy. Br J Haematol 106(2):377–384
Nakao S, Takamatsu H, Chuhjo T, Ueda M, Shiobara S, Matsuda T, Kaneshige T, Mizoguchi H (1994) Identification of a specific HLA class II haplotype strongly associated with susceptibility to cyclosporine-dependent aplastic anemia. Blood 84(12):4257–4261
Sugimori C, Chuhjo T, Feng XM, Yamazaki H, Takami A, Teramura M, Mizoguchi H, Omine M, Nakao S (2006) Minor population of CD55(-)CD59(-) blood cells predicts response to immunosuppressive therapy and prognosis in patients with aplastic anemia. Blood 107(4):1308–1314. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-06-2485
Sugimori C, Yamazaki H, Feng XM, Mochizuki K, Kondo Y, Takami A, Chuhjo T, Kimura A, Teramura M, Mizoguchi H, Omine M, Nakao S (2007) Roles of DRB1*1501 and DRB1*1502 in the pathogenesis of aplastic anemia. Exp Hematol 35(1):13–20. doi:10.1016/j.exphem.2006.09.002
Berger T, Rubner P, Schautzer F, Egg R, Ulmer H, Mayringer I, Dilitz E, Deisenhammer F, Reindl M (2003) Antimyelin antibodies as a predictor of clinically definite multiple sclerosis after a first demyelinating event. N Engl J Med 349(2):139–145
Ronkainen MS, Harkonen T, Perheentupa J, Knip M (2005) Characterization of the humoral immune response to glutamic acid decarboxylase in patients with autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) and/or type 1 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol 153(6):901–906. doi:10.1530/eje.1.02026
Feng XM, Chuhjo T, Sugimori C, Kotani T, Lu XZ, Takami A, Takamatsu H, Yamazaki H, Nakao S (2004) Diazepam-binding inhibitor-related protein 1: a candidate autoantigen in acquired aplastic anemia patients harboring a minor population of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria-type cells. Blood 104(8):2425–2431. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-05-1839
Takamatsu H, Feng XM, Chuhjo T, Lu XZ, Sugimori C, Okawa K, Yamamoto M, Iseki S, Nakao S (2007) Specific antibodies to moesin, a membrane-cytoskeleton linker protein, are frequently detected in patients with acquired aplastic anemia. Blood 109(6):2514–2520. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-07-036715
Nyman TA, Rosengren A, Syyrakki S, Pellinen TP, Rautajoki K, Lahesmaa R (2001) A proteome database of human primary T helper cells. Electrophoresis 22(20):4375–4382
Jensen ON, Podtelejnikov A, Mann M (1996) Delayed extraction improves specificity in database searches by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization peptide maps. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 10(11):1371–1378
Yates JR (1998) Mass spectrometry and the age of the proteome. J Mass Spectrom 33(1):1–19
Camitta BM (2000) What is the definition of cure for aplastic anemia? Acta Haematol 103(1):16–18
Caporali R, Bugatti S, Bruschi E, Cavagna L, Montecucco C (2005) Autoantibodies to heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Autoimmunity 38(1):25–32. doi:10.1080/08916930400022590
Hassfeld W, Steiner G, Hartmuth K, Kolarz G, Scherak O, Graninger W, Thumb N, Smolen JS (1989) Demonstration of a new antinuclear antibody (anti-RA33) that is highly specific for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 32(12):1515–1520
GA DA, Vretou E, Sekeris CE (1988) Autoantibodies to the core proteins of hnRNPs. FEBS Lett 231(1):118–124
KE JL, Wilson SH, Steinberg AD, Klinman DM (1988) Antibodies from patients and mice with autoimmune diseases react with recombinant hnRNP core protein A1. J Autoimmun 1(1):73–83
Montecucco C, Caporali R, Negri C, de Gennaro F, Cerino A, Bestagno M, Cobianchi F, Astaldi-Ricotti GC (1990) Antibodies from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus recognize different epitopes of a single heterogeneous nuclear RNP core protein. Possible role of cross-reacting antikeratin antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 33(2):180–186
Steiner G, Hartmuth K, Skriner K, Maurerfogy I, Sinski A, Thalmann E, Hassfeld W, Barta A, Smolen JS (1992) Purification and partial sequencing of the nuclear autoantigen RA33 shows that it is indistinguishable from the A2 protein of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex. J Clin Investig 90(3):1061–1066
Hassfeld W, Steiner G, Studnickabenke A, Skriner K, Graninger W, Fischer I, Smolen JS (1995) Autoimmune response to the spliceosome. An immunologic link between rheumatoid arthritis, mixed connective tissue disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 38(6):777–785
Jones DA, Yawalkar N, Suh KY, Sadat S, Rich B, Kupper TS (2004) Identification of autoantigens in psoriatic plaques using expression cloning. J Investig Dermatol 123(1):93–100. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22709.x
Bomsztyk K, VanSeuningen I, Suzuki H, Denisenko O, Ostrowski J (1997) Diverse molecular interactions of the hnRNP K protein. FEBS Lett 403(2):113–115
Bomsztyk K, Denisenko O, Ostrowski J (2004) HnRNP K: One protein multiple processes. Bioessays 26(6):629–638. doi:10.1002/bies.20048
Mandal M, Vadlamudi R, Nguyen D, Wang RA, Costa L, Bagheri-Yarmand R, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R (2001) Growth factors regulate heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K expression and function. J Biol Chem 276(13):9699–9704
Li C, Hong Y, Tan YX, Zhou H, Ai JH, Li SJ, Zhang L, Xia QC, Wu JR, Wang HY, Zeng R (2004) Accurate qualitative and quantitative proteomic analysis of clinical hepatocellular carcinoma using laser capture microdissection coupled with isotope-coded affinity tag and two-dimensional liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 3(4):399–409. doi:10.1074/mcp.M300133-MCP200
Hatakeyama H, Kondo T, Fujii K, Nakanishi Y, Kato H, Fukuda S, Hirohashi S (2006) Protein clusters associated with carcinogenesis, histological differentiation and nodal metastasis in esophageal cancer. Proteomics 6(23):6300–6316. doi:10.1002/pmic.200600488
Klimek-Tomczak K, Mikula M, Dzwonek A, Paziewska A, Karczmarski J, Hennig E, Bujnicki JM, Bragoszewski P, Denisenko O, Bomsztyk K, Ostrowski J (2006) Editing of hnRNP K protein mRNA in colorectal adenocarcinoma and surrounding mucosa. Br J Cancer 94(4):586–592. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602938
Notari M, Neviani P, Santhanam R, Blaser BW, Chang JS, Galietta A, Willis AE, Roy DC, Caligiuri MA, Marcucci G, Perrotti D (2006) A MAPK/HNRPK pathway controls BCR/ABL oncogenic potential by regulating MYC mRNA translation. Blood 107(6):2507–2516. doi:10.1182/blood-2005.09.3732
Valai A, Belisova A, Hayer S, Hoefler E, Steiner G (2004) The RNA binding domains of hnRNP K contain major autoepitopes targeted by patients with SLE and other autoimmune diseases. In: ICI/FOCISed. Abstract number 1148
Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Levy M, Shapiro S (eds) (1991) The drug etiology of agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia: the international agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia study. Oxford University Press, New York
Wagatsuma M, Kimura M, Suzuki R, Takeuchi F, Matsuta K, Watanabe H (1996) Ezrin, radixin and moesin are possible autoimmune antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol 33(15):1171–1176
Hansen PB, Lauritzen AMF (2005) Aplastic anemia successfully treated with rituximab. Am J Hematol 80(4):292–294. doi:10.1002/ajh.20428
Castiglioni MG, Scatena P, Pandolfo C, Mechelli S, Bianchi M (2006) Rituximab therapy of severe aplastic anemia induced by fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in a patient affected by B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 47(9):1985–1986. doi:10.1080/10428190600709630
Fritsch R, Eselbock D, Skriner K, Jahn-Schmid B, Scheinecker C, Bohle B, Tohidast-Akrad M, Hayer S, Neumuller J, Pinol-Roma S, Smolen JS, Steiner G (2002) Characterization of autoreactive T cells to the autoantigens heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2 (RA33) and filaggrin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 169(2):1068–1076
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank R. Oumi and T. Tanaka of Cellular Transplantation Biology of Kanazawa University who provided some technical assistance and all of the BMF study groups who provided sera of patients to this study. This work was supported by a grant from Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Technology, Sports and Culture of Japan (KAKENHI No. 21390291) and grants from the Research Committee for Idiopathic Hematopoietic Disorders, the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Z., Takamatsu, H., Espinoza, J.L. et al. Autoantibodies specific to hnRNP K: a new diagnostic marker for immune pathophysiology in aplastic anemia. Ann Hematol 89, 1255–1263 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-1020-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-1020-3