Abstract
Objects
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), the enzyme that converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins, is overexpressed in a variety of tumors, including medulloblastoma (MB). CD133, a transmembrane glycoprotein, has been suggested as a marker for cancer stem cells in brain tumors. The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of celecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, in enhancing the effects of ionizing radiotherapy (IR) on medulloblastoma-derived CD133-positive cells (MB-CD133+).
Materials and methods
MB-CD133+ were isolated from two medulloblastoma cell lines (Daoy and UW228). Then, they were treated with celecoxib in different concentrations, and cell viability was assessed. The assays of cell survival, soft agar, radiosensitivity, colony formation, and apoptotic activity in MB-CD133+ treated with celecoxib alone, radiation alone, or celecoxib combined with radiation were further evaluated.
Results
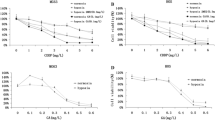
MB-CD133+ showed the self-renew ability to form sphere bodies in vitro and regenerate tumors in vivo. The levels of COX-2 mRNA and protein in MB-CD133+ were significantly higher than those in MB-CD133−. The treatment of 30 μM celecoxib could effectively inhibit the abilities of cell proliferation and colony formation and increase IR-induced apoptosis in treated MB-CD133+. Furthermore, in vivo study demonstrated that celecoxib significantly enhanced radiosensitivity in MB-CD133+-transplanted grafts. Notably, xenotransplantation analysis demonstrated that the treatment of celecoxib could further suppress the expressions of angiogenic and stemnness-related genes in treated MB-CD133+ grafts of SCID mice.
Conclusions
Celecoxib presents the potential of radiosensitizing effect in MB-derived cancer stem cells. Therefore, it should be warranted in future trials to enhance the radiotherapeutic effects in MB patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonarakis E, Heath E, Walczak J, Nelson W, Fedor H, De Marzo A, Zahurak M, Piantadosi S, Dannenberg A, Gurganus R (2009) Phase II, randomized. Placebo-controlled trial of neoadjuvant celecoxib in men with clinically localized prostate cancer: evaluation of drug-specific biomarkers. J Clin Oncol 27:4986
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon R, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland A, Dewhirst M, Bigner D, Rich J (2006) Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444:756–760
Baryawno N, Sveinbjornsson B, Eksborg S, Orrego A, Segerstrom L, Oqvist C, Holm S, Gustavsson B, Kagedal B, Kogner P (2008) Tumor-growth-promoting cyclooxygenase-2 prostaglandin E2 pathway provides medulloblastoma therapeutic targets. Neuro-oncology 10:661
Beier D, Hau P, Proescholdt M, Lohmeier A, Wischhusen J, Oefner P, Aigner L, Brawanski A, Bogdahn U, Beier C (2007) CD133+ and CD133-glioblastoma-derived cancer stem cells show differential growth characteristics and molecular profiles. Cancer Res 67:4010
Calabrese C, Poppleton H, Kocak M, Hogg TL, Fuller C, Hamner B, Oh EY, Gaber MW, Finklestein D, Allen M, Frank A, Bayazitov IT, Zakharenko SS, Gajjar A, Davidoff A, Gilbertson RJ (2007) A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell 11:69–82
Cervoni L, Cantore G (1995) Medulloblastoma in pediatric age: a single-institution review of prognostic factors. Childs Nerv Syst 11:80–84, discussion 85
Chen J, Chen Y, SU Y, Tseng S (2007) Celecoxib increased expression of 14-3-3U and induced apoptosis of glioma cells. Anticancer Res 27:2547
Chen Y, Hsu H, Chen Y, Tsai T, How C, Wang C, Hung S, Chang Y, Tsai M, Lee Y (2008) Oct-4 expression maintained cancer stem-like properties in lung cancer-derived CD133-positive cells. PLoS One 3:e2637
Chiou S, Kao C, Lin H, Tseng W, Liu R, Chung C, Ku H, Lin C, Wong T (2006) Monitoring the growth effect of xenotransplanted human medulloblastoma in an immunocompromised mouse model using in vitro and ex vivo green fluorescent protein imaging. Childs Nerv Syst 22:475–480
Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N, Radovanovic I, Ruiz i Altaba A (2007) HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and tumorigenicity. Curr Biol 17:165–172
Collins A, Berry P, Hyde C, Stower M, Maitland N (2005) Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate cancer stem cells. Cancer Res 65:10946
Dannenberg AJ, Altorki NK, Boyle JO, Dang C, Howe LR, Weksler BB, Subbaramaiah K (2001) Cyclo-oxygenase 2: a pharmacological target for the prevention of cancer. Lancet Oncol 2:544–551
Debucquoy A, Devos E, Vermaelen P, Landuyt W, De Weer S, Van Den Heuvel F, Haustermans K (2009) 18F-FLT and 18F-FDG PET to measure response to radiotherapy combined with celecoxib in two colorectal xenograft models. Int J Radiat Biol 85:763–771
Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, Pilozzi E, Biffoni M, Di Virgilio A, Conticello C, Ruco L, Peschle C, De Maria R (2007) Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ 15:504–514
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, Fiocco R, Foroni C, Dimeco F, Vescovi A (2004) Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res 64:7011
Gangemi RM, Griffero F, Marubbi D, Perera M, Capra MC, Malatesta P, Ravetti GL, Zona GL, Daga A, Corte G (2009) SOX2 silencing in glioblastoma tumor-initiating cells causes stop of proliferation and loss of tumorigenicity. Stem Cells 27:40–48
Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, Roberts HR, Williams AC, Paraskeva C, Kaidi A (2009) The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis 30:377–386
Grosch S, Tegeder I, Niederberger E, Brautigam L, Geisslinger G (2001) COX-2 independent induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells by the selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib. FASEB J 15:2742–2744
Grosch S, Maier T, Schiffmann S, Geisslinger G (2006) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-independent anticarcinogenic effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst 98:736
Habrand JL, De Crevoisier R (2001) Radiation therapy in the management of childhood brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 17:121–133
Hambardzumyan D, Becher OJ, Rosenblum MK, Pandolfi PP, Manova-Todorova K, Holland EC (2008) PI3K pathway regulates survival of cancer stem cells residing in the perivascular niche following radiation in medulloblastoma in vivo. Genes Dev 22:436–448
Hoppe-Hirsch E, Brunet L, Laroussinie F, Cinalli G, Pierre-Kahn A, Renier D, Sainte-Rose C, Hirsch JF (1995) Intellectual outcome in children with malignant tumors of the posterior fossa: influence of the field of irradiation and quality of surgery. Childs Nerv Syst 11:345, discussion 345–346
Kang K, Wang T, Woon C, Cheah E, Moore X, Zhu C, Wong M (2007) Enhancement of glioblastoma radioresponse by a selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib: inhibition of tumor angiogenesis with extensive tumor necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:888–896
Kao C, Chiou S, Chen Y, Singh S, Lin H, Liu R, Lo C, Yang C, Chi C, Lee C (2005) Increased expression of osteopontin gene in atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system. Mod Pathol 18:769–778
Kawamori T, Rao C, Seibert K, Reddy B (1998) Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, against colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 58:409
Kesari S, Schiff D, Henson J, Muzikansky A, Gigas D, Doherty L, Batchelor T, Longtine J, Ligon K, Weaver S (2008) Phase II study of temozolomide, thalidomide, and celecoxib for newly diagnosed glioblastoma in adults. Neuro-oncology 10:300
Kuipers G, Slotman B, Wedekind L, Stoter T, van den Berg J, Sminia P, Lafleur M (2007) Radiosensitization of human glioma cells by cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibition: independent on COX-2 expression and dependent on the COX-2 inhibitor and sequence of administration. Int J Radiat Biol 83:677–685
Liu X, Yao S, Kirschenbaum A, Levine A (1998) NS398, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, induces apoptosis and down-regulates bcl-2 expression in LNCaP cells. Cancer Res 58:4245
Lu K, Chen Y, Tsai P, Tsai M, Lee Y, Chiang C, Kao C, Chiou S, Ku H, Lin C (2009) Evaluation of radiotherapy effect in resveratrol-treated medulloblastoma cancer stem-like cells. Childs Nerv Syst 25:543–550
Mantovani G, Maccio A, Madeddu C, Gramignano G, Lusso M, Serpe R, Massa E, Astara G, Deiana L (2006) A phase II study with antioxidants, both in the diet and supplemented, pharmaconutritional support, progestagen, and anti-cyclooxygenase-2 showing efficacy and safety in patients with cancer-related anorexia/cachexia and oxidative stress. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 15:1030
Masferrer J, Leahy K, Koki A, Zweifel B, Settle S, Woerner B, Edwards D, Flickinger A, Moore R, Seibert K (2000) Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Cancer Res 60:1306
McAdam B, Catella-Lawson F, Mardini I, Kapoor S, Lawson J, FitzGerald G (1999) Systemic biosynthesis of prostacyclin by cyclooxygenase (COX)-2: the human pharmacology of a selective inhibitor of COX-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:272
Milas L (2003) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme inhibitors and radiotherapy: preclinical basis. Am J Clin Oncol 26:S66
Mutter R, Lu B, Carbone D, Csiki I, Moretti L, Johnson D, Morrow J, Sandler A, Shyr Y, Ye F (2009) A phase II study of celecoxib in combination with paclitaxel, carboplatin, and radiotherapy for patients with inoperable stage IIIA/B non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15:2158
O’Brien C, Pollett A, Gallinger S, Dick J (2006) A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature 445:106–110
Pakos E, Ioannidis J (2004) Radiotherapy vs. nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of heterotopic ossification after major hip procedures: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60:888–895
Patrawala L, Calhoun T, Schneider-Broussard R, Zhou J, Claypool K, Tang D (2005) Side population is enriched in tumorigenic, stem-like cancer cells, whereas ABCG2+ and ABCG2-cancer cells are similarly tumorigenic. Cancer Res 65:6207
Pawlik T, Keyomarsi K (2004) Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:928–942
Pawlik T, Keyomarsi K (2004) Colon carcinoma radiosensitivity and cell cycle arrest is dependent on both p53/p21 status and radiation dose. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 2004:310
Prince M, Sivanandan R, Kaczorowski A, Wolf G, Kaplan M, Dalerba P, Weissman I, Clarke M, Ailles L (2007) Identification of a subpopulation of cells with cancer stem cell properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:973
Singh S, Clarke I, Terasaki M, Bonn V, Hawkins C, Squire J, Dirks P (2003) Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 63:5821
Singh S, Hawkins C, Clarke I, Squire J, Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman R, Cusimano M, Dirks P (2004) Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 432:396–401
Sutter R, Shakhova O, Bhagat H, Behesti H, Sutter C, Penkar S, Santuccione A, Bernays R, Heppner FL, Schuller U, Grotzer M, Moch H, Schraml P, Marino S (2010) Cerebellar stem cells act as medulloblastoma-initiating cells in a mouse model and a neural stem cell signature characterizes a subset of human medulloblastomas. Oncogene 29:1845–1856
Vescovi A, Galli R, Reynolds B (2006) Brain tumour stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer 6:425–436
Whelan HT, Krouwer HG, Schmidt MH, Reichert KW, Kovnar EH (1998) Current therapy and new perspectives in the treatment of medulloblastoma. Pediatr Neurol 18:103–115
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by research grants from the National Science Council (NSC-98-3111-B-075-001-MY3), Chi Mei Medical Center (CMYM 9801), Taipei Veterans General Hospital (V97E1-008, V97F-001), Yen-Tjing-Ling Medical Foundation (95/96/97/98), Taipei City Hospital (96001-62-014, 96001-62-018, 96002-62-092, and 97001-62-003) and National Yang-Ming University (Ministry of Education, Aim for the Top University Plan), and Technology Development Program for Academia (98-EC-17-A-19-S2-0107), Department of Industrial Technology, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Kuan-Hsuan Chen, Chuan-Chih Hsu, and Wen-Shin Song contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, KH., Hsu, CC., Song, WS. et al. Celecoxib enhances radiosensitivity in medulloblastoma-derived CD133-positive cells. Childs Nerv Syst 26, 1605–1612 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1190-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1190-2