Abstract
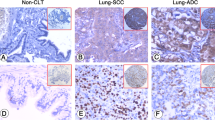
Purpose: The aim of this study was to assess the prognostic relevance of apoptotic index (AI), considered alone or together with expression of several proteins controlling G1 check point (p53, mdm2, pRb and p21WAF1/CIP1) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Methods: Study group included 50 NSCLC patients who underwent curative pulmonary resection. Apoptosis was detected with the use of TUNEL technique and AI was defined as the number of apoptotic cells per 1,000 tumor cells. The expression of p53, mdm2, pRb and p21WAF1/CIP1 was assessed immunohistochemically. Results: The mean and median AI calculated for all 50 patients was 14 and 9, respectively. Patients with lower (<14) and higher (≥14) AI constituted 35 (70%) and 15 (30%) of cases, respectively. AI was not correlated with patient clinical characteristics, and expression of p53, pRb and p21WAF1/CIP1 . However, lower AI was correlated with over-expression of mdm2 protein (P=0.04). Median survival for patients with lower and higher AI was 43 months and 22 months, respectively, and 5-year survival probability—60 and 25%, respectively (P=0.03). In multivariate analysis, the only variable associated with shortened survival was AI (P=0.03, HR=2.9, 95% CI 1.95–3.86). Conclusions: These results suggest that AI correlates with mdm2 protein expression and influences survival in NSCLC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
el-Deiry WS, Harper JW, O’Connor PM, Velculescu VE, Canman CE, Jackman J, Pietenpol JA, Burrell M, Hill DE, Wang Y (1994) WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res 54:1169–1174
Hanaoka T, Nakayama J, Haniuda M, Sato TA (2002) Immunohistochemical demonstration of apoptosis-regulated proteins, Bcl-2 and Bax, in resected non-small-cell lung cancers. Int J Clin Oncol 7:152–158
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K, Elledge SJ (1993) The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 75:805–816
Harris CC (1996) Structure and function of the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues for rational cancer therapeutic strategies. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1442–1455
Hsieh JK, Chan FS, O’Connor DJ, Mittnacht S, Zhong S, Lu X (1999) RB regulates the stability and the apoptotic function of p53 via MDM2. Mol Cell 3:181–193
Kerr JFR, Winterford CM, Harmon BV (1994) Apoptosis: its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 73:2013–2026
Kotelnikov VM, Coon JS, Mundle S, Kelanic S, La Follette S, Taylor S IV, Hutchinson J, Panje W, Caldarelli DD, Preisler HD (1997) Cyclin D1 expression in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck and in oral mucosa in relation to proliferation and apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res 3:95–101
Lane DP (1992) Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 358:15–16
Langendijk H, Thunnissen E, Arends JW, de Jong J, ten Velde G, Lamers R, Guinee D, Holden J, Wouters M (2000) Cell proliferation and apoptosis in stage III inoperable non-small cell lung carcinoma treated by radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 56:197–207
Levine AJ, Momand J, Finlay CA (1991) The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature 351:453–456
Li R, Waga S, Hannon GJ, Beach D, Stillman B (1994) Differential effects by the p21 CDK inhibitor on PCNA-dependent DNA replication and repair. Nature 371:534–537
Macluskey M, Baillie R, Chandrachud LM, Pendleton N, Schor AM (2000) High levels of apoptosis are associated with improved survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 20:2123–2128
Matturri L, Colombo B, Lavezzi AM (1999) Evidence for apoptosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Relationship with cell kinetics and prognosis. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 21:240–244
Momand J, Zambetti GP (1997) Mdm2: ”Big Brother” of p53. J Cell Biochem 64:343–352
Piette J, Neel H, Marechal V (1997) Mdm2: keeping p53 under control. Oncogene 15:1001–1010
Prives C, Hall PA (1999) The p53 pathway. J Pathol 187:112–126
Puglisi F, Minisini AM, Aprile G, Barbone F, Cataldi P, Artico D, Damante G, Beltrami CA, Di Loreto C (2002) Balance between cell division and cell death as predictor of survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncology 63:76–83
Pulkkanen KJ, Laukkanen MO, Naarala J, Yla-Herttuala S (2000) False-positive apoptosis signal in mouse kidney and liver detected with TUNEL assay. Apoptosis 5:329–333
Roninson IB (2002) Oncogenic functions of tumour suppressor p21(Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1): association with cell senescence and tumour-promoting activities of stromal fibroblasts. Cancer Lett 179:1–14
Shiina H, Igawa M, Shigeno K, Yamasaki Y, Urakami S, Yoneda T, Wada Nagasaki, Honda S, Nagasaki M (1999) Clinical significance of mdm2 and p53 expression in bladder cancer. A comparison with cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncology 56:239–247
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (1997) TNM classification of malignant tumors. UICC International Union Against Cancer. Wiley-Liss, New York
Soini Y, Pääkkö P, Lehto VP (1998) Histopathological evaluation of apoptosis in cancer. Am J Pathol 153:1041–1053
Tanaka F, Takata T, Yamada T, Yanagihara K, Otake Y, Miyahara R, Nakagawa T, Kawano Y, Ishikawa S, Inui K, Wada H (2002) Apoptotic tumor-cell death in response to cell proliferation is influenced by p53 status in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 36:27–32
Törmänen U, Eerola AK, Rainio P, Vähäkangas K, Soini Y, Sormunen R, Bloigu R, Lehto VP, Paakko P (1995) Enhanced apoptosis predicts shortened survival in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 55:5595–5602
Yap DB, Hsieh JK, Chan FS, Lu X (1999) mdm2: a bridge over the two tumour suppressors, p53 and Rb. Oncogene 18:7681–7689
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dworakowska, D., Jassem, E., Jassem, J. et al. Clinical significance of apoptotic index in non-small cell lung cancer: correlation with p53, mdm2, pRb and p21WAF1/CIP1 protein expression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131, 617–623 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0010-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0010-7