Abstract
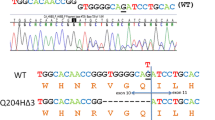
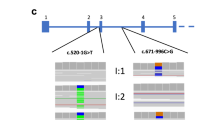
Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is a low-penetrant autosomal dominant disorder caused by mutations in the hydroxymethylbilane synthase (HMBS) gene. Direct detection of mutations is becoming the method of choice for the accurate identification of asymptomatic affected individuals within AIP families so that they can be advised to avoid drugs and other compounds that provoke the life-threatening acute neurovisceral crises that characterise the condition. We describe a prospective comparison of direct automated sequencing of cDNA (29 patients) or genomic DNA (28 patients) to identify HMBS mutations in 57 patients referred consecutively for mutational analysis; 39 different mutations were identified in 54 patients. The sensitivity of the cDNA and genomic DNA methods was 69% and 95%, respectively, indicating that analysis of genomic DNA provides a higher mutation detection rate. Thirty mutations were restricted to a single family; only one (R173W) occurred in more than three families. Of the mutations (6 missense, 8 splice defects, 10 frameshifts, 1 nonsense), 25 have not been reported previously. One novel mutation (344+33G→T) was located in a putative intron splice enhancer in intron 7. Our results define the extent of allelic heterogeneity and the types (41% missense; 59% truncating) and distribution (35% in exons 10, 12, 14) of HMBS mutations, for AIP in the United Kingdom.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 January 1999 / Accepted: 19 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whatley, S., Woolf, J. & Elder, G. Comparison of complementary and genomic DNA sequencing for the detection of mutations in the HMBS gene in British patients with acute intermittent porphyria: identification of 25 novel mutations. Hum Genet 104, 505–510 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050995
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050995