Abstract
Background: The purpose of the present study was to examine the expression of cell cycle regulators [p53, p21WAF1/CIP1 (p21), and Rb] and apoptosis related proteins Bax and Bcl-XL and to evaluate the relationship between their expressions and clinicopathological findings in patients with superficial squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus.
Methods: We immunohistochemically investigated the expression of p53, p21, Rb, Bax, and Bcl-XL in 79 patients with superficial esophageal carcinoma.
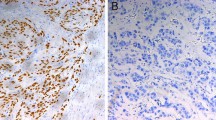
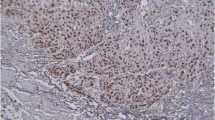
Results: p21 overexpression was found in mucosal carcinoma (P = 0.05) and a high Bcl-XL score was observed for submucosal carcinoma (P = 0.03). The patients with high Bcl-XL score had more frequent lymphatic invasion and lymph node metastasis than did those with low Bcl-XL score (P < 0.05). Univariate analysis revealed significantly shorter survival in patients with high Bcl-XL expression than in those with low Bcl-XL expression, but Bcl-XL expression was not identified as an independent prognostic factor by multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: Because Bcl-Xl expression correlated well with depth of tumor invasion, lymphatic invasion, and lymph node metastasis, examination of Bcl-XL expression will help to estimate the properties in superficial squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Reed JC. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 1994; 124: 1–6.
Vaux DL. Toward an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of physiological cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1993; 90: 786–9.
Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 1995; 267: 1456–62.
Oltvai ZN, Korsmeyer SJ. Checkpoints of dueling dimers foil death wishes. Cell 1994; 79: 189–92.
Oltvai ZN, Milliman C, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 1993; 74: 609–19.
Sato T, Hanada M, Bodrug S, et al. Interactions among members of the bcl-2 protein family analyzed with a yeast two-hybrid system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994; 91: 9238–42.
Hanada M, Aime-Sempe C, Sato T, Reed JC. Structure-function analysis of bcl-2 protein: identification of conserved domains important for homodimerization with bcl-2 and heterodimerization with bax. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 11962–8.
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ. Bad: a heterodimeric partner for Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces bax and promotes cell death. Cell 1995; 80: 285–91.
Farrow SN, White JHM, Martinou I, et al. Cloning of a bcl-2 homologue by interaction with adenovirus E1B 19K. Nature 1995; 374: 731–3.
Chittenden T, Harrington EA, O’Conner R, et al. Induction of apoptosis by the Bcl-2 homologue Bak. Nature 1995; 374: 733–6.
Kiefer MC, Brauer MJ, Powers VC, et al. Modulation of apoptosis by the widely distributed Bcl-2 homologue Bak. Nature 1995; 374: 736–9.
Bodrug SE, Aime-Sempe C, Sato T, Krajewski S, Hanada M, Reed JC. Biochemical and functional comparisons of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 proteins: evidence for a novel mechanism of regulating Bcl-2 family protein function. Cell Death Differ 1995; 2: 173–82.
Kuzumaki T, Kobayashi T, Ishikawa K. Genistein induces p21 (Cip1/WAF1) expression and blocks the G1 to S phase transition in mouse fibroblast and melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998; 251: 291–5.
Sobin LH, Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumors. International Union Against Cancer. 5th edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1997.
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 1981; 29: 577–80.
Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Epstein JI, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of bcl-2, bax, bcl-X, and mcl-1 expression in prostate cancers. Am J Pathol 1996; 148: 1567–76.
Wang LD, Zhou Q, Hong JY, Qiu SL, Yang CS. p53 protein accumulation and gene mutations in multifocal esophageal precancerous lesions from symptom free subjects in a high incidence area for esophageal carcinoma in Henan, China. Cancer 1996; 77: 1244–9.
Natsugoe S, Nakashima S, Matsumoto M, et al. Expression of p21WAF1/CIP1 in the p53-dependent pathway is related to prognosis in patients with advanced esophageal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 2445–9.
Hashimoto N, Tachibana M, Dhar DK, Yoshimura H, Nagasue N. Expression of p53 and Rb proteins in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: their relationship with clinicopathologic characteristics. Ann Surg Oncol 1999; 6: 489–94.
Chino O, Makuuchi H, Shimada H, Machimura T, Mitomi T, Osamura Y. Assessment of the proliferative activity of superficial esophageal carcinoma using MIB-1 immunostaining for the Ki-67 antigen. J Surg Oncol 1998; 67: 18–24.
Torzewski M, Sarbia M, Heep H, Dutkowski P, Willers R, Gabbert HE. Expression of Bcl-XL, an antiapoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family, in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 1998; 4: 577–83.
Pena JC, Thompson CB, Recant W, Vokes EE, Rudin CM. Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer 1999; 85: 164–70.
Maurer CA, Friess H, Buhler SS, et al. Apoptosis inhibiting factor Bcl-xL might be the crucial member of the Bcl-2 gene family in colorectal cancer. Dig Dis Sci 1998; 43: 2641–8.
Kondo S, Shinomura Y, Kanayama S, et al. Over-expression of bcl-xL gene in human gastric adenomas and carcinomas. Int J Cancer 1996; 68: 727–30.
Friess H, LuZ, Andren-Sandberg A, et al. Moderate activation of the apoptosis inhibitor bcl-xL worsens the prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg 1998; 228: 780–7.
Olopade OI, Adeyanju MO, Safa AR, et al. Overexpression of Bcl-x protein in primary breast cancer is associated with high tumor grade and nodal metastases. Cancer J Sci Am 1997; 3: 230–7.
Krajewski S, Blomqvist C, Franssila K, et al. Reduced expression of proapoptotic gene Bax is associated with poor response rates to combination chemotherapy and shorter survival in women with metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 4471–8.
Xie X, Clausen OPF, De Angelis P, Boysen M. Bax expression has prognostic significance that is enhanced when combined with AgNOR counts in glottic carcinomas. Br J Cancer 1998; 78: 100–5.
Ogura E, Senzaki H, Yamamoto D, et al. Prognostic significance of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL/S, Bax and Bak expressions in colorectal carcinomas. Oncol Rep 1999; 6: 365–9.
Marx D, Binder C, Meden H, et al. Differential expression of apoptosis associated genes bax and bcl-2 in ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res 1997; 17: 2233–40.
Koshida Y, Saegusa M, Okayasu I. Apoptosis, cell proliferation and expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in gastric carcinomas: immunohistochemical and clinicopathological study. Br J Cancer 1997; 75: 367–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, M., Natsugoe, S., Nakashima, S. et al. Clinical Significance and Prognostic Value of Apoptosis Related Proteins in Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 8, 598–604 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10434-001-0598-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10434-001-0598-z