Abstract
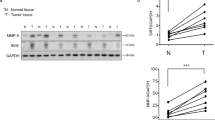
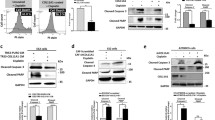
High levels of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein have been associated with invasion and metastasis of breast tumors. Both prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) have been shown to mediate the invasive activity of COX-2 in breast cancer cells. Here we expand these studies to determine how COX-2 uses PGE2 and IL-8 to induce breast cancer cell invasion. We demonstrated that PGE2 and IL-8 decreased the expression of the tumor suppressor protein Programmed Cell Death 4 (PDCD4). We hypothesized that suppression of PDCD4 expression is vital to the invasive activity of PGE2 and IL-8. In MCF-7 cells overexpressing PDCD4 (MCF-7/PDCD4), PGE2 and IL-8 failed to induce invasion, in contrast to the parental MCF-7 cells, thus indicating that PDCD4 blocks breast cancer cell invasion. MCF-7/PDCD4 cells produced higher levels of the Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) than the parental cells. Silencing TIMP-2 mRNA in MCF-7/PDCD4 cells reversed the anti-invasive effects of PDCD4, allowing PGE2 and IL-8 to induce the invasion of these cells. Here we report the novel findings that suppression of PDCD4 expression is vital for the invasive activity of COX-2 mediated by PGE2 and IL-8, and that PDCD4 increases TIMP-2 expression to inhibit breast cancer cell invasion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ries L, Melbert D, Krapcho M et al (2007) SEER Cancer Statistic Review, 1975–2004, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD. Available via INTERNET http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2004/, based on November 2006 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, 2007. Cited 2 Feb 2007
Denkert C, Winzer KJ, Muller BM et al (2003) Elevated expression of cyclooxygenase-2 is a negative prognostic factor for disease free survival and overall survival in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer 97(12):2978–2987
Ristimaki A, Sivula A, Lundin J et al (2002) Prognostic significance of elevated cyclooxygenase-2 expression in breast cancer. Cancer Res 62(3):632–635
Soslow RA, Dannenberg AJ, Rush D et al (2000) COX-2 is expressed in human pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors. Cancer 89(12):2637–2645
Larkins TL, Nowell M, Singh S et al (2006) Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 decreases breast cancer cell motility, invasion and matrix metalloproteinase expression. BMC Cancer 6:181–193
Simeone AM, Nieves-Alicea R, McMurtry VC et al (2007) Cyclooxygenase-2 uses the protein kinase C/interleukin-8/urokinase-type plasminogen activator pathway to increase the invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol 30(4):785–792
Singh B, Berry JA, Shoher A et al (2005) COX-2 overexpression increases motility and invasion of breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol 26(5):1393–1399
Zhang Z, DuBois RN (2001) Detection of differentially expressed genes in human colon carcinoma cells treated with a selective COX-2 inhibitor. Oncogene 20(33):4450–4456
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Nair R et al (2001) A novel transformation suppressor, Pdcd4, inhibits AP-1 transactivation but not NF-kappaB or ODC transactivation. Oncogene 20(6):669–676
Cmarik JL, Min H, Hegamyer G et al (1999) Differentially expressed protein Pdcd4 inhibits tumor promoter-induced neoplastic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(24):14037–14042
Jansen AP, Camalier CE, Colburn NH (2005) Epidermal expression of the translation inhibitor programmed cell death 4 suppresses tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 65(14):6034–6041
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Komar AA et al (2003) The transformation suppressor Pdcd4 is a novel eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A binding protein that inhibits translation. Mol Cell Biol 23(1):26–37
Goke R, Barth P, Schmidt A et al (2004) Programmed cell death protein 4 suppresses CDK1/cdc2 via induction of p21(Waf1/Cip1). Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287(6):C1541–C1546
Jansen AP, Camalier CE, Stark C et al (2004) Characterization of programmed cell death 4 in multiple human cancers reveals a novel enhancer of drug sensitivity. Mol Cancer Ther 3(2):103–110
Chen Y, Knosel T, Kristiansen G et al (2003) Loss of PDCD4 expression in human lung cancer correlates with tumour progression and prognosis. J Pathol 200(5):640–646
Ma G, Guo KJ, Zhang H et al (2005) Expression of programmed cell death 4 and its clinicopathological significance in human pancreatic cancer. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 27(5):597–600
Zhang H, Ozaki I, Mizuta T et al (2006) Involvement of programmed cell death 4 in transforming growth factor-beta1-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 25(45):6101–6112
Mudduluru G, Medved F, Grobholz R et al (2007) Loss of programmed cell death 4 expression marks adenoma-carcinoma transition, correlates inversely with phosphorylated protein kinase B, and is an independent prognostic factor in resected colorectal cancer. Cancer 110(8):1697–1707
Gao F, Zhang P, Zhou C et al (2007) Frequent loss of PDCD4 expression in human glioma: possible role in the tumorigenesis of glioma. Oncol Rep 17(1):123–128
Wen YH, Shi X, Chiriboga L et al (2007) Alterations in the expression of PDCD4 in ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncol Rep 18(6):1387–1393
Leupold JH, Yang HS, Colburn NH et al (2007) Tumor suppressor Pdcd4 inhibits invasion/intravasation and regulates urokinase receptor (u-PAR) gene expression via Sp-transcription factors. Oncogene 26(31):4550–4562
Yang HS, Matthews CP, Clair T et al (2006) Tumorigenesis suppressor Pdcd4 down-regulates mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 1 expression to suppress colon carcinoma cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol 26(4):1297–1306
Wang Q, Sun Z, Yang HS (2008) Downregulation of tumor suppressor Pdcd4 promotes invasion and activates both beta-catenin/Tcf and AP-1-dependent transcription in colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene 27(11):1527–1535
Tari AM, Simeone AM, Li YJ et al (2005) Cyclooxygenase-2 protein reduces tamoxifen and N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide inhibitory effects in breast cancer cells. Lab Invest 85(11):1357–1367
Ahn SM, Jeong SJ, Kim YS et al (2004) Retroviral delivery of TIMP-2 inhibits H-ras-induced migration and invasion in MCF10A human breast epithelial cells. Cancer Lett 207(1):49–57
Yoneda T, Sasaki A, Dunstan C et al (1997) Inhibition of osteolytic bone metastasis of breast cancer by combined treatment with the bisphosphonate ibandronate and tissue inhibitor of the matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Clin Invest 99(10):2509–2517
Sacco MG, Cato EM, Ceruti R et al (2001) Systemic gene therapy with anti-angiogenic factors inhibits spontaneous breast tumor growth and metastasis in MMTVneu transgenic mice. Gene Ther 8(1):67–70
Ree AH, Florenes VA, Berg JP et al (1997) High levels of messenger RNAs for tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1 and TIMP-2) in primary breast carcinomas are associated with development of distant metastases. Clin Cancer Res 3(9):1623–1628
Vizoso FJ, Gonzalez LO, Corte MD et al (2007) Study of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 96(6):903–911
Jiang Y, Goldberg ID, Shi YE (2002) Complex roles of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in cancer. Oncogene 21(14):2245–2252
Dorrello NV, Peschiaroli A, Guardavaccaro D et al (2006) S6K1- and betaTRCP-mediated degradation of PDCD4 promotes protein translation and cell growth. Science 314(5798):467–471
Ozpolat B, Akar U, Steiner M et al (2007) Programmed cell death-4 tumor suppressor protein contributes to retinoic acid-induced terminal granulocytic differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cells. Mol Cancer Res 5(1):95–108
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A et al (2008) Programmed Cell Death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the MicroRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283(2):1026–1033
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, et al (2007) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. Advance online publication October 29
Acknowledgements
We thank Vanity McMurtry and Wendy Schober for their technical assistance. This work was supported in part by the Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation (to AMT) and the Cancer Center Core Grant CA16672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nieves-Alicea, R., Colburn, N.H., Simeone, AM. et al. Programmed Cell Death 4 inhibits breast cancer cell invasion by increasing Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-2 expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 114, 203–209 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-9993-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-9993-5