Abstract
Introduction
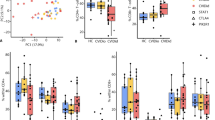
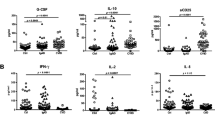
Common variable immunodeficiency is a heterogeneous antibody deficiency syndrome with autoimmune and inflammatory complications in a significant proportion of patients. The study was designed to evaluate the role of T regulatory (Treg) cells in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) patients with autoimmunity.
Methods
The number and frequency of Treg cells (CD4+, CD25hi, Foxp3+) were evaluated in patients and controls, and Foxp3 expression in different subgroups of CVID patients with common clinical manifestations was compared.
Results
CVID patients had significantly fewer Treg cells than controls, and low frequency of Treg cells was associated with expansion of CD21lo B cells in patients. Patients with autoimmunity had significantly reduced frequency but normal numbers of regulatory T cells, whilst patients with splenomegaly had significant reduction in frequency and number of regulatory T cells.
Conclusion
Foxp3 is useful on its own or as an adjunct to classify CVID patients although the possibility of reduction in Treg cells as a secondary phenomenon cannot be excluded.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosen F, Eibl M, Fischer A, Volanakis J, Aiuti F, Notarangelo L, et al. Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of an IUIS Scientific Committee. International Union of Immunological Societies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999;118(Suppl 1):1–28.
Wehr C, Kivioja T, Schmitt C, Ferry B, Witte T, Eren E, et al. The EUROclass trial: defining subgroups in common variable immunodeficiency. Blood. 2008;111(1):77–85.
Bacchelli C, Buckridge S, Thrasher AJ, Gaspar HB. Translational mini-review series on immunodeficiency: molecular defects in common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;149(3):401–9.
Cunningham-Rundles C, Bodian C. Common variable immunodeficiency: clinical and immunological features of 248 patients. Clin Immunol. 1999;92(1):34–48.
Bryant A, Calver NC, Toubi E, Webster AD, Farrant J. Classification of patients with common variable immunodeficiency by B cell secretion of IgM and IgG in response to anti-IgM and interleukin-2. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990;56(2):239–48.
Warnatz K, Denz A, Drager R, Braun M, Groth C, Wolff-Vorbeck G, et al. Severe deficiency of switched memory B cells (CD27(+)IgM(−)IgD(−)) in subgroups of patients with common variable immunodeficiency: a new approach to classify a heterogeneous disease. Blood. 2002;99(5):1544–51.
Piqueras B, Lavenu-Bombled C, Galicier L, Bergeron-van-der Cruyssen F, Mouthon L, Chevret S, et al. Common variable immunodeficiency patient classification based on impaired B cell memory differentiation correlates with clinical aspects. J Clin Immunol. 2003;23(5):385–400.
Carsetti R, Rosado MM, Donnanno S, Guazzi V, Soresina A, Meini A, et al. The loss of IgM memory B cells correlates with clinical disease in common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115(2):412–7.
Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow ME, Ferguson PJ, Whitesell L, et al. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet. 2001;27(1):20–1.
Chatila TA, Blaeser F, Ho N, Lederman HM, Voulgaropoulos C, Helms C, et al. JM2, encoding a fork head-related protein, is mutated in X-linked autoimmunity-allergic disregulation syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2000;106(12):R75–81.
Wildin RS, Ramsdell F, Peake J, Faravelli F, Casanova JL, Buist N, et al. X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy syndrome is the human equivalent of mouse scurfy. Nat Genet. 2001;27(1):18–20.
Nik Tavakoli N, Hambly BD, Sullivan DR, Bao S. Forkhead box protein 3: essential immune regulatory role. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40:2369–73.
Shevach EM. Regulatory T cells in autoimmmunity*. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:423–49.
Dejaco C, Duftner C, Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Schirmer M. Imbalance of regulatory T cells in human autoimmune diseases. Immunology. 2006;117(3):289–300.
Torgerson TR. Regulatory T cells in human autoimmune diseases. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006;28(1):63–76.
Conley ME, Notarangelo LD, Etzioni A. Diagnostic criteria for primary immunodeficiencies. Representing PAGID (Pan-American Group for Immunodeficiency) and ESID (European Society for Immunodeficiencies). Clin Immunol. 1999;93(3):190–7.
Gorg C, Weide R, Schwerk WB. Malignant splenic lymphoma: sonographic patterns, diagnosis and follow-up. Clin Radiol. 1997;52(7):535–40.
Warnatz K, Wehr C, Drager R, Schmidt S, Eibel H, Schlesier M, et al. Expansion of CD19(hi)CD21(lo/neg) B cells in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) patients with autoimmune cytopenia. Immunobiology. 2002;206(5):502–13.
Kingsley CI, Karim M, Bushell AR, Wood KJ. CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells prevent graft rejection: CTLA-4- and IL-10-dependent immunoregulation of alloresponses. J Immunol. 2002;168(3):1080–6.
Edinger M, Hoffmann P, Ermann J, Drago K, Fathman CG, Strober S, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells preserve graft-versus-tumor activity while inhibiting graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation. Nat Med. 2003;9(9):1144–50.
Fevang B, Yndestad A, Sandberg WJ, Holm AM, Muller F, Aukrust P, et al. Low numbers of regulatory T cells in common variable immunodeficiency: association with chronic inflammation in vivo. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;147(3):521–5.
Yu GP, Chiang D, Song SJ, Hoyte EG, Huang J, Vanishsarn C, et al. Regulatory T cell dysfunction in subjects with common variable immunodeficiency complicated by autoimmune disease. Clin Immunol. 2009;131:240–53.
Horn J, Manguiat A, Berglund LJ, Knerr V, Tahami F, Grimbacher B, et al. Decrease in phenotypic regulatory T cells in subsets of patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;156(3):446–54.
de Kleer IM, Wedderburn LR, Taams LS, Patel A, Varsani H, Klein M, et al. CD4+CD25bright regulatory T cells actively regulate inflammation in the joints of patients with the remitting form of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Immunol. 2004;172(10):6435–43.
Cao D, van Vollenhoven R, Klareskog L, Trollmo C, Malmstrom V. CD25brightCD4+ regulatory T cells are enriched in inflamed joints of patients with chronic rheumatic disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(4):R335–46.
Takahashi T, Tagami T, Yamazaki S, Uede T, Shimizu J, Sakaguchi N, et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells constitutively expressing cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4. J Exp Med. 2000;192(2):303–10.
Wing K, Onishi Y, Prieto-Martin P, Yamaguchi T, Miyara M, Fehervari Z, et al. CTLA-4 control over Foxp3+ regulatory T cell function. Science. 2008;322(5899):271–5.
Zheng Y, Manzotti CN, Burke F, Dussably L, Qureshi O, Walker LS, et al. Acquisition of suppressive function by activated human CD4+ CD25- T cells is associated with the expression of CTLA-4 not FoxP3. J Immunol. 2008;181(3):1683–91.
Ephrem A, Chamat S, Miquel C, Fisson S, Mouthon L, Caligiuri G, et al. Expansion of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by intravenous immunoglobulin: a critical factor in controlling experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Blood. 2008;111(2):715–22.
Kessel A, Ammuri H, Peri R, Pavlotzky ER, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy affects T regulatory cells by increasing their suppressive function. J Immunol. 2007;179(8):5571–5.
De Groot AS, Moise L, McMurry JA, Wambre E, Van Overtvelt L, Moingeon P, et al. Activation of natural regulatory T cells by IgG Fc-derived peptide “Tregitopes”. Blood. 2008;112(8):3303–11.
Fearon DT, Carroll MC. Regulation of B lymphocyte responses to foreign and self-antigens by the CD19/CD21 complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:393–422.
Griffioen AW, Franklin SW, Zegers BJ, Rijkers GT. Expression and functional characteristics of the complement receptor type 2 on adult and neonatal B lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993;69(1):1–8.
Rakhmanov M, Keller B, Gutenberger S, Foerster C, Hoenig M, Driessen G, et al. Circulating CD21low B cells in common variable immunodeficiency resemble tissue homing, innate-like B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(32):13451–6.
Wehr C, Eibel H, Masilamani M, Illges H, Schlesier M, Peter HH, et al. A new CD21low B cell population in the peripheral blood of patients with SLE. Clin Immunol. 2004;113(2):161–71.
Warnatz K, Schlesier M. Flowcytometric phenotyping of common variable immunodeficiency. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2008;74(5):261–71.
Sanchez-Ramon S, Radigan L, Yu JE, Bard S, Cunningham-Rundles C. Memory B cells in common variable immunodeficiency: clinical associations and sex differences. Clin Immunol. 2008;128(3):314–21.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank John Toolan and Kate Ford for their help in sample collection, June Cole for technical assistance and patients and controls from St. James’s University hospital for agreeing to take part in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugakani, G., Wood, P.M.D. & Carter, C.R.D. Frequency of Treg Cells Is Reduced in CVID Patients with Autoimmunity and Splenomegaly and Is Associated with Expanded CD21lo B Lymphocytes. J Clin Immunol 30, 292–300 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9351-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9351-3