Abstract
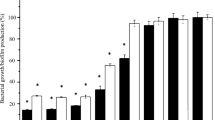
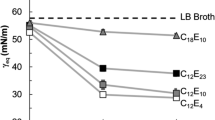
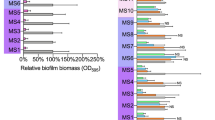
The ability of surfactants obtained from three Lactobacillus acidophilus strains to inhibit Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermidis biofilms was evaluated. Their influence was determined on bacterial initial adhesion, biofilm formation and dispersal using MTT-reduction assay, confocal laser scanning microscopy and image PHLIP analysis. The number of adhering S. aureus and S. epidermidis cells after a 3-h co-incubation with biosurfactants was reduced by 5–56 % in a strain-and dose-dependent manner. S. epidermidis-and, to a lower extent, in S. aureus-biofilm formation was also inhibited in the presence of the tested surfactants. The addition of surfactants to preformed mature biofilms accelerated their dispersal, and changed the parameters of biofilm morphology. The L. acidophilus-derived surfactants inhibit bacterial deposition rate and biofilm development (and also its maturation) without affecting cell growth probably due to the influence on the cell-surface hydrophobicity of staphylococci.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LAA:
-
Lactobacillus acidophilus
- SAU:
-
Staphylococcus aureus
- SEP:
-
Staphylococcus epidermidis
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- CFU:
-
colony-forming unit(s)
- CLSM:
-
confocal laser scanning microscopy
- CSH:
-
cell-surface hydrophobicity
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- MRS:
-
De Man-Rogosa-Sharpe (broth)
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffered saline
- PHLIP:
-
phobia laser scanning microscopy imaging processor
- SAT:
-
salt-aggregation test
- TSB:
-
tryptic-soy broth
- TSBGlc:
-
TSB with 0.25 % d-glucose
References
Bêhal V.: Mode of action of microbial bioactive metabolites. Folia Microbiol. 51, 359–369 (2006).
Bodour A.A., Miller-Maier R.M.: Application of a modified drop-collapse technique for surfactant quantitation and screening of biosurfactant-producing microorganisms. J.Microbiol.Meth. 32, 273–280 (1998).
Doyle R.J.: Contribution of the hydrophobic effect to microbial infection. Microb.Infect. 2, 391–400 (2000).
Espinosa-Urgel M.: Resident parking only: rhamnolipids maintain fluid channels in biofilm. J.Bacteriol. 185, 699–700 (2003).
Goetz F.: Staphylococcus and biofilms. Mio.Microbiol. 43, 1367–1378 (2002).
Hall-Stoodley L., Costerton J.W., Stoodley P.: Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nature Rev. 2, 95–106 (2004).
VAN Hoogmoed C.G., Van Der Kuijl-Booij M., Van Der Mei H.C., Busscher H.J.: Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans NS adhesion to glass with and without a salivary conditioning film by biosurfactant-releasing Streptococcus mitis strains. Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 66, 659–663 (2000).
Horošová K., Bujñáková D., Kmeť V.: Effect of lactobacilli on E. coli adhesion to Caco-2 cells in vitro. Folia Microbiol. 51, 281–282 (2006).
Lewis K.: Riddle of biofilm resistance. Antimicrob.Agents Chemother. 45, 999–1007 (2001).
Mireles J.R. II, Toguchi A., Harshey R.M.: Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium swarming mutants with altered biofilm-forming abilities: surfactin inhibits biofilm formation. J.Bacteriol. 183, 5848–5854 (2001).
Mack D., Becker P., Chatterje I., Dobinsky S., Knobloch J.K.-M., Peter G., Rohde H., Herrmann M.: Mechanisms of biofilm formation in Staphylococus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus: functional molecules, regulatory circuits, and adaptive responses. Internat.J.Med.Microbiol. 294, 203–212 (2004).
Merk K., Borelli C., Korting H.C.: Lactobacilli — bacteria-host interactions with special regard to the urogenital tract. Internat. J.Med.Microbiol. 295, 9–18 (2005).
Mueller L.N., De Brouwer J.F.C., Almeida J.S., Stal L.J., Xavier J.B.: Analysis of a marine phototrophic biofilm by confocal laser scanning microscopy using the new image quantification software PHLIP. MMC Ecology 6, 1–15 (2006).
Ofek I., Hasty D.L. Sharon N.: Anti-adhesion therapy of bacterial diseases: prospects and problems. FEMS Immunol.Med.Microbiol. 38, 181–191 (2003).
Reid G., Burton J.: Use of Lactobacillus to prevent infection by pathogenic bacteria. Microb.Infect. 4, 319–324 (2002).
Reid G., Tieszer C., Lam D.: Influence of lactobacilli on the adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans to fibers and epithelial cells. J.Ind.Microbiol. 15, 248–253 (1995).
Rodrigues L., Van Der Mei H., Banat I.M., Teixeira J., Oliveira R.: Biosurfactant from Lactococcus lactis 53 inhibits microbial adhesion on silicone rubber. Appl.Genet.Molec.Biotech. 66, 306–311 (2004a).
Rodrigues L., Van Der Mei H., Banat I.M., Teixeira J., Oliveira R.: Influence of biosurfactants from probiotic bacteria on formation of biofilms on voice prostheses. Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 70, 4408–4410 (2004b).
Rodrigues L., Van Der Mei H., Banat I.M., Teixeira J., Oliveira R.: Inhibition of microbial adhesion to silicone rubber treated with biosurfactant from Streptococcus thermophilus A. FEMS Immunol.Med.Microbiol., 46, 107–112 (2006a).
Rodrigues L., Banat I.M., Teixeira J., Oliveira R.: Biosurfactants: potential applications in medicine. J.Antimicrob.Chemother. 57, 609–618 (2006b).
Růžička F., Holá V., Votava M., Tejkalová R., Horvát R., Heroldová M., Woznicová V.: Biofilm detection and the clinical significance of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates. Folia Microbiol. 49, 75–78 (2004).
Shintani H.: Modification of medical device surface to attain anti-infection. Trends Biomater.Artif.Organs 18, 1–8 (2004).
Singh P., Cameotra S.S.: Potential applications of microbial surfactants in biomedical sciences. Trends Microbiol. 22, 142–146 (2004).
Trebichavský I., Šplíchal I.: Probiotics manipulate host cytokine response and induce antimicrobial peptides. Folia Microbiol. 51, 507–510 (2004).
Velraeds M.W., Van Der Mei H.C., Reid G., Busscher H.J.: Inhibition of initial adhesion of uropathogenic Enterococcus faecalis by biosurfactants from Lactobacillus isolates. Appl.Eviron.Microbiol. 62, 1958–1963 (1996).
Velraeds M.W., Van De Belt-Gritter B., Van Der Mei H.C., Reid G., Busscher H.J.: Interference in initial adhesion of uropathogenic bacteria and yeasts to silicone rubber by a Lactobacillus acidophilus biosurfactant. J.Med.Microbiol. 47, 1081–1085 (1998).
Vesterlund S., Karp M., Salminen S., Ouwehand A.C.: Staphylococus aureus adheres to human intestinal mucus but can be displaced by certain lactic acid bacteria. Microbiology 152, 1819–1826 (2006).
Walencka E., Sadowska B., Różalska S., Hryniewicz W., Różalska B.: Staphylococcus aureus biofilm as a target for single or repeated doses of oxacillin, vancomycin, linezolid and/or lysostaphin. Folia Microbiol. 51, 381–386 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walencka, E., Różalska, S., Sadowska, B. et al. The influence of Lactobacillus acidophilus-derived surfactants on staphylococcal adhesion and biofilm formation. Folia Microbiol 53, 61–66 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-008-0009-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-008-0009-y