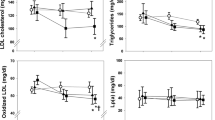
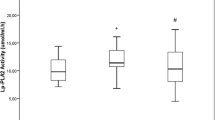
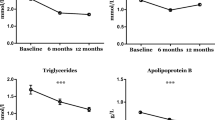
Background: Serum Lipoprotein A [Lp(a)] is considered an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Reduction of other risk factors such as serum triglycerides and serum cholesterol is seen after weight reduction but it has been difficult to demonstrate a similar reduction of Lp(a). In this study Lp(a) is studied following weight reduction after intestinal bypass surgery for obesity. Methods: A cross-sectional study was performed in which Lp(a) levels were compared between patients operated with intestinal bypass surgery for obesity (bilio-intestinal bypass) and a closely matched control group. The controls were chosen so as to correspond to the operated patients' preoperative body mass indices. Results: The operated group had reduced their body mass index from a mean of 42 kg/m2 to a mean of 29 kg/m2 and had a significantly lower mean serum Lp(a) level (113 mg/l, SEM 34) than controls (207 mg/l, SEM 37), p < 0.05. Conclusion: Lowered Lp(a) levels are correlated to substantial weight loss following intestinal bypass surgery for obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boman, L., Ericson, M. Lipoprotein A Levels after Intestinal Bypass Operation for Morbid Obesity. OBES SURG 7, 125–127 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1381/096089297765556006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1381/096089297765556006